7
Note the following:
• XenServer labels its AD entry on the AD database using its hostname. Therefore, if two XenServer hosts have
the same hostname and are joined to the same AD domain, the second XenServer will overwrite the AD entry
of the first XenServer, regardless of if they are in the same or in different pools, causing the AD authentication
on the first XenServer to stop working.
It is possible to use the same hostname in two XenServer hosts, as long as they join different AD domains.
• The XenServer hosts can be in different time-zones, as it is the UTC time that is compared. To ensure
synchronization is correct, you may choose to use the same NTP servers for your XenServer pool and the Active
Directory server.
• Mixed-authentication pools are not supported (that is, you cannot have a pool where some servers in the pool
are configured to use Active Directory and some are not).
• The XenServer Active Directory integration uses the Kerberos protocol to communicate with the Active
Directory servers. Consequently, XenServer does not support communicating with Active Directory servers that
do not utilize Kerberos.
• For external authentication using Active Directory to be successful, it is important that the clocks on your
XenServer hosts are synchronized with those on your Active Directory server. When XenServer joins the Active
Directory domain, this will be checked and authentication will fail if there is too much skew between the
servers.
Warning:
Host names must consist solely of no more than 63 alphanumeric characters, and must not
be purely numeric.
Once you have Active Directory authentication enabled, if you subsequently add a server to that pool, you are
prompted to configure Active Directory on the server joining the pool. When you are prompted for credentials
on the joining server, enter Active Directory credentials with sufficient privileges to add servers to that domain.
Active Directory integration
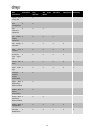
Make sure that the following firewall ports are open for outbound traffic in order for XenServer to access the
domain controllers.
Port Protocol Use
53 UDP/TCP DNS
88 UDP/TCP Kerberos 5
123 UDP NTP
137 UDP NetBIOS Name Service
139 TCP NetBIOS Session (SMB)
389 UDP/TCP LDAP
445 TCP SMB over TCP
464 UDP/TCP Machine password changes
3268 TCP Global Catalog Search
Note:
To view the firewall rules on a Linux computer using iptables, run the following command:
iptables - nL