74
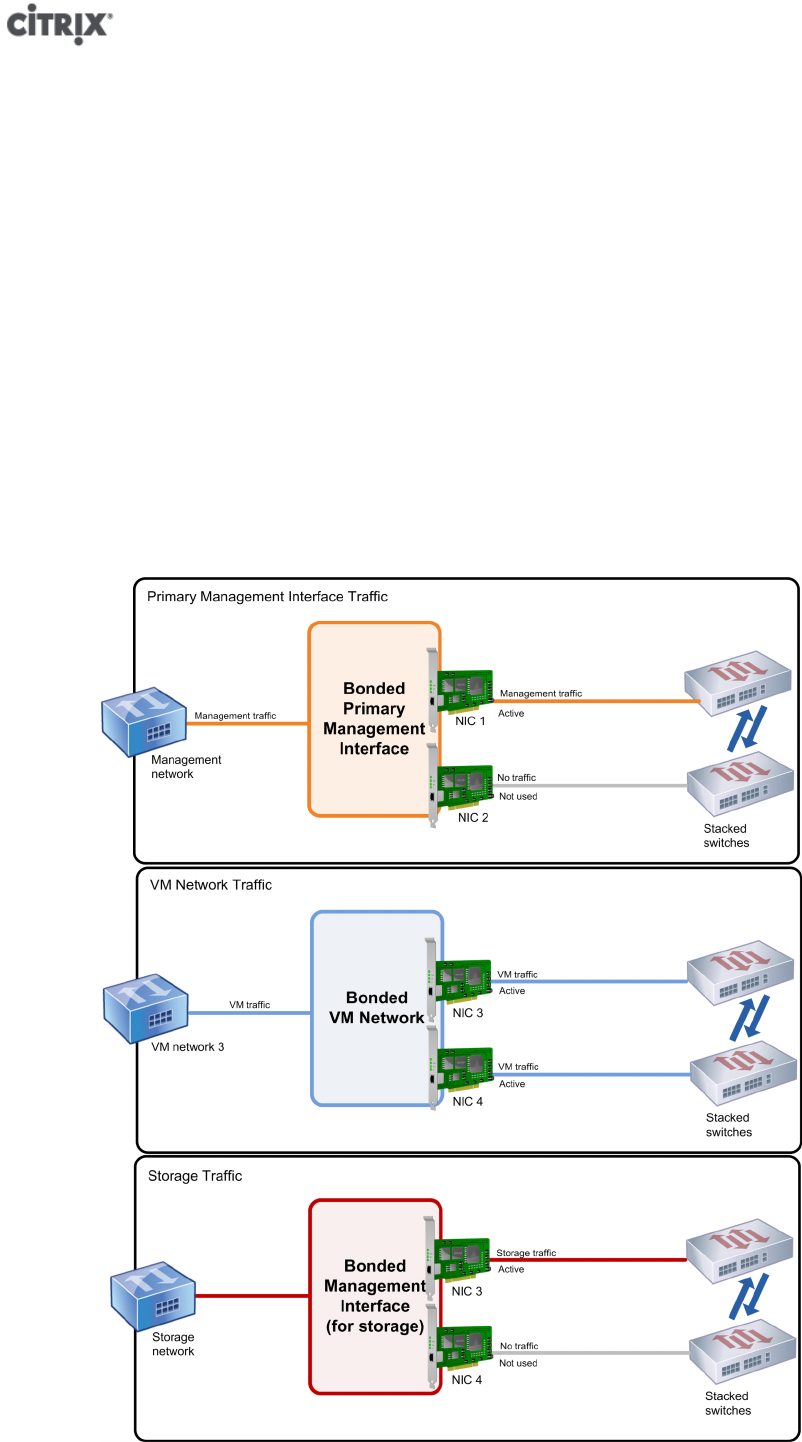
This illustration shows how two NICs in a bonded pair use the same network settings, as represented
by the networks in each host. The NICs in the bonds connect to different switches for redundancy.
Active-Active Bonding
Active-Active, which is the default bonding mode, is an active/active configuration for guest traffic: both NICs
can route VM traffic simultaneously. When bonds are used for management traffic, only one NIC in the bond can
route traffic: the other NIC remains unused and provides fail-over support.
For VM traffic, active-active mode also balances traffic. However, it is important to note that "balance" refers to
the quantity (MB) of data routed on the NIC. When XenServer rebalances traffic, it simply changes which VM's
traffic (more precisely, which VIF's traffic) is carried across which NIC.
While NIC bonding can provide load balancing for traffic from multiple VMs, it cannot provide a single VM with
the throughput of two NICs. Any given VIF only uses one of the links in a bond at a time. As XenServer rebalances
traffic, VIFs are not permanently assigned to a specific NIC in the bond. However, for VIFs with high throughput,
periodic rebalancing ensures that the load on the links is approximately equal.
The illustration that follows shows the differences between the three different types of interfaces that you can
bond.


















