67
Xen Memory Usage
When calculating the memory footprint of a Xen host there are two components that must be taken into
consideration. First there is the memory consumed by the Xen hypervisor itself; then there is the memory
consumed by the control domain of the host. The control domain is a privileged VM that provides low-level
services to other VMs, such as providing access to physical devices. It also runs the management tool stack.
Setting Control Domain Memory
If your control domain requires more allocated memory, this can be set using the Xen CLI.
Use the xe vm-memory-target-set command to set the amount of memory available to the control domain.
The xe vm-memory-target-wait command can be used to check if the control domain is currently at the requested
memory target specified at the last use of the xe vm-memory-target-set command. xe vm-memory-target-wait
will not return until the actual memory usage of the control domain is at the target, or will time out if the target
cannot be reached, for example when the target is lower than the actual memory requirements of the VM.
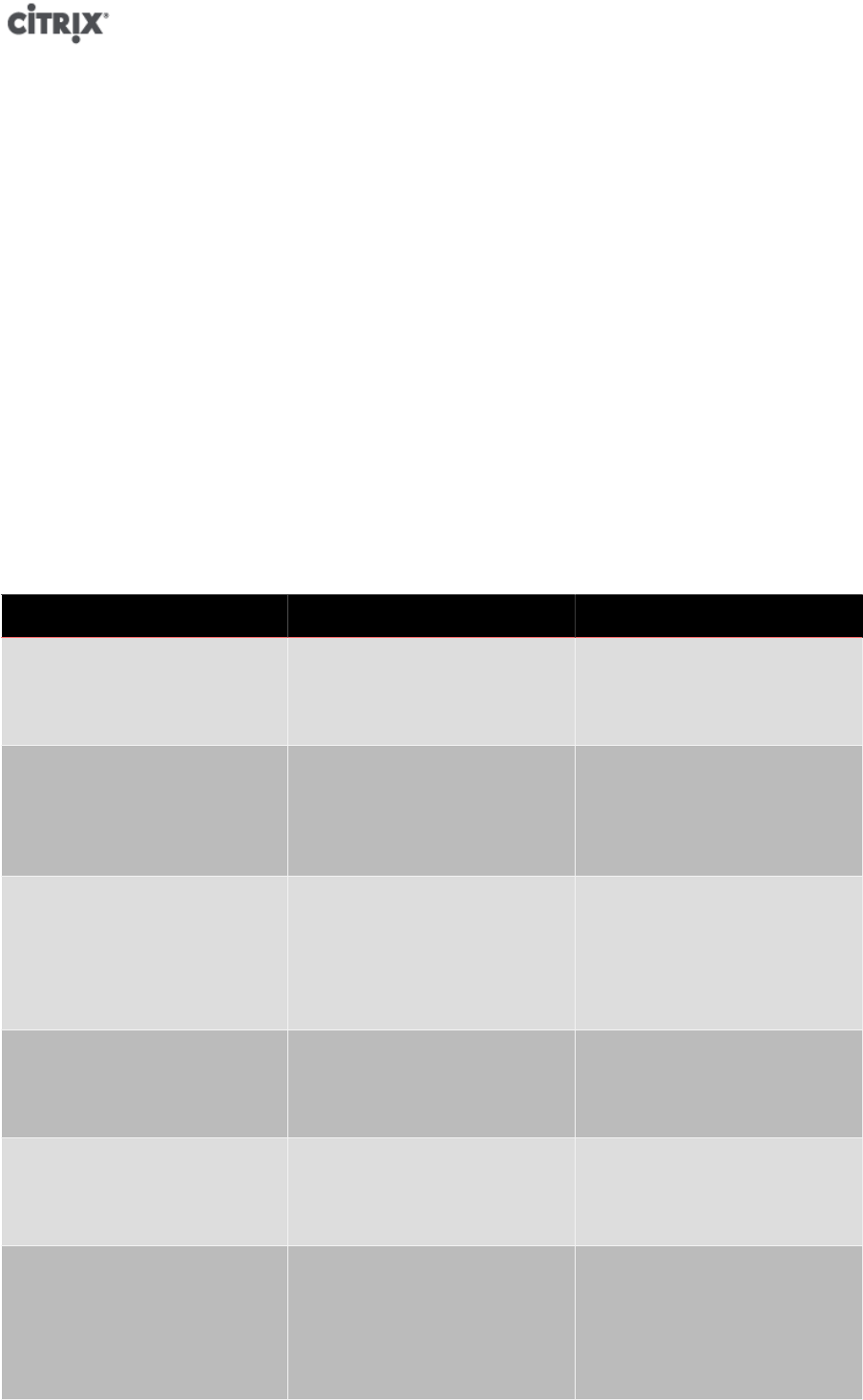
The following fields on a VM define how much memory will be allocated. The default values shown are indicative
of a machine with 8 GB of RAM:
name default description
memory-actual 411041792 The actual amount of memory
current available for use by the VM
Read Only
memory-target 411041792 The target amount of memory
as set by using xe vm-memory-
target-set
Read Only
memory-static-max 790102016 The maximum possible physical
memory
Read Write when the VM is
suspended; Read Only when the
VM is running
memory-dynamic-max 790102016 The desired maximum memory to
be made available
Read Write
memory-dynamic-min 306184192 The desired minimum memory to
be made available
Read Write
memory-static-min 306184192 The minimum possible physical
memory
Read Write when the VM is
suspended; Read Only when the
VM is running