135
Dialogic
®
SS7G2x Signaling Server SGW Mode User Manual Issue 4
Chapter 7: Configuration Overview
This section provides an overview of the various components that are used in the configuration of a Dialogic
®
SS7G2x Signaling Gateway and how these components relate to each other. The Signaling Gateway
configuration is described in the following categories:
• System and Hardware – The configuration of system Ethernet addresses, signaling boards and PCMs.
• Signaling – The transmission of messages on the SS7 and IP side.
• Routing – The route SS7 messages take through the gateway.
• Management – Bringing entities in and out of service and monitoring system status.
• Dual Resilient Operation – Two Signaling Gateways acting as a single Point Code.
• MTP Default Routing – Allocation of a default route to MTP.
7.1 System, Hardware and Signaling Configuration
7.1.1 System Configuration
Each Signaling Gateway contains four Ethernet ports allowing it to communicate with four separate IP
networks. The Ethernet interface is used for the transfer of SS7 signaling information over IP, for telnet
communication with the management interface and the transfer of files (such as those for software update
and configuration backup) using ftp between the Signaling Gateway and a remote server. The fourth IP
network (IPADDR4) is reserved for management only and cannot be used for SIGTRAN operation.
A Signaling Gateway can be given a presence within an IP network using its first Ethernet port configured
with an IP Address (IPADDR) and a Subnet Mask (SUBNET). If the Signaling Gateway is communicating with
a destination that is not on the local subnet, a default IP gateway (GATEWAY) can be configured.
Optionally, the Signaling Gateway can be given a presence in up to two more subnets using additional
Ethernet ports configured with a an IP addresses ((IPADDR2 or IPADDR3) and additional subnet masks
(SUBNET2 or SUBNET3).
System level configuration is configured using the CNSYx set of commands.
Potentially the user may require communication with different IP gateways to reach other IP networks.
Additional IP Gateways can be configured using the IPGWx set of commands.
After changing the IP configuration of a Signaling Gateway, it should be restarted using the MNRSI
command.
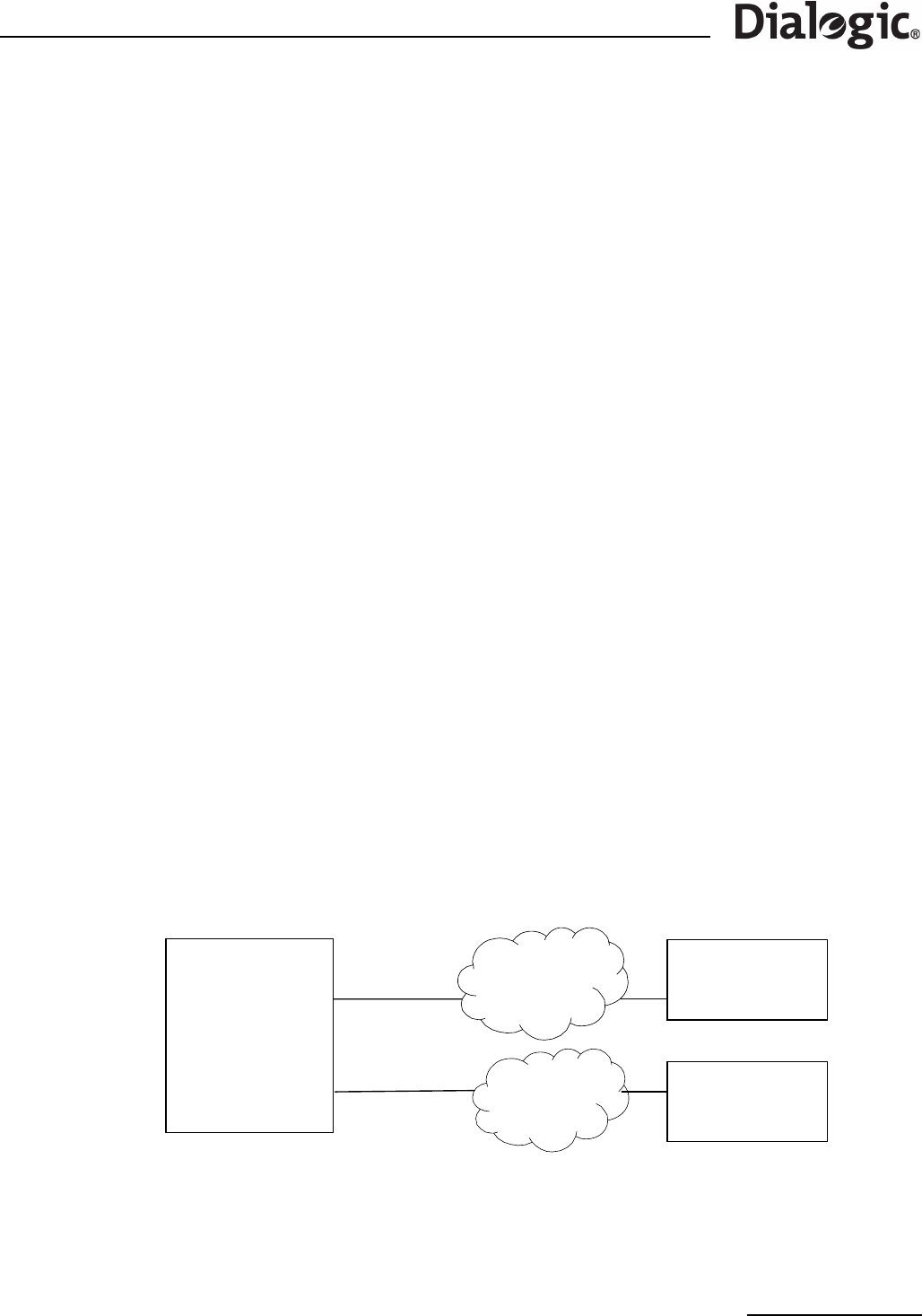
Figure 4. Multiple IP Networks
Figure 4 demonstrates the Signaling Gateway configured to exist in multiple IP networks. Example MML for
the above configuration is:
CNSYS:IPADDR=193.145.185.151,SUBNET=255.255.255.0;
CNSYS:IPADDR2=173.132.73.122,SUBNET2=255.255.255.0;
CNSYS:GATEWAY=193.145.185.149;
MNRSI;
193.145.185.151
173.132.73.122
Second IP
Network
IP Gateway
173.132.73.21
First IP
Network
Default IP
Gateway
193.145.185.149
Signaling
Gateway


















