Intel
®
IXP45X and Intel
®
IXP46X Product Line of Network Processors—Category
Intel
®
IXP45X and Intel
®
IXP46X Product Line of Network Processors
HDD February 2007
80 Document Number: 305261, Revision: 004
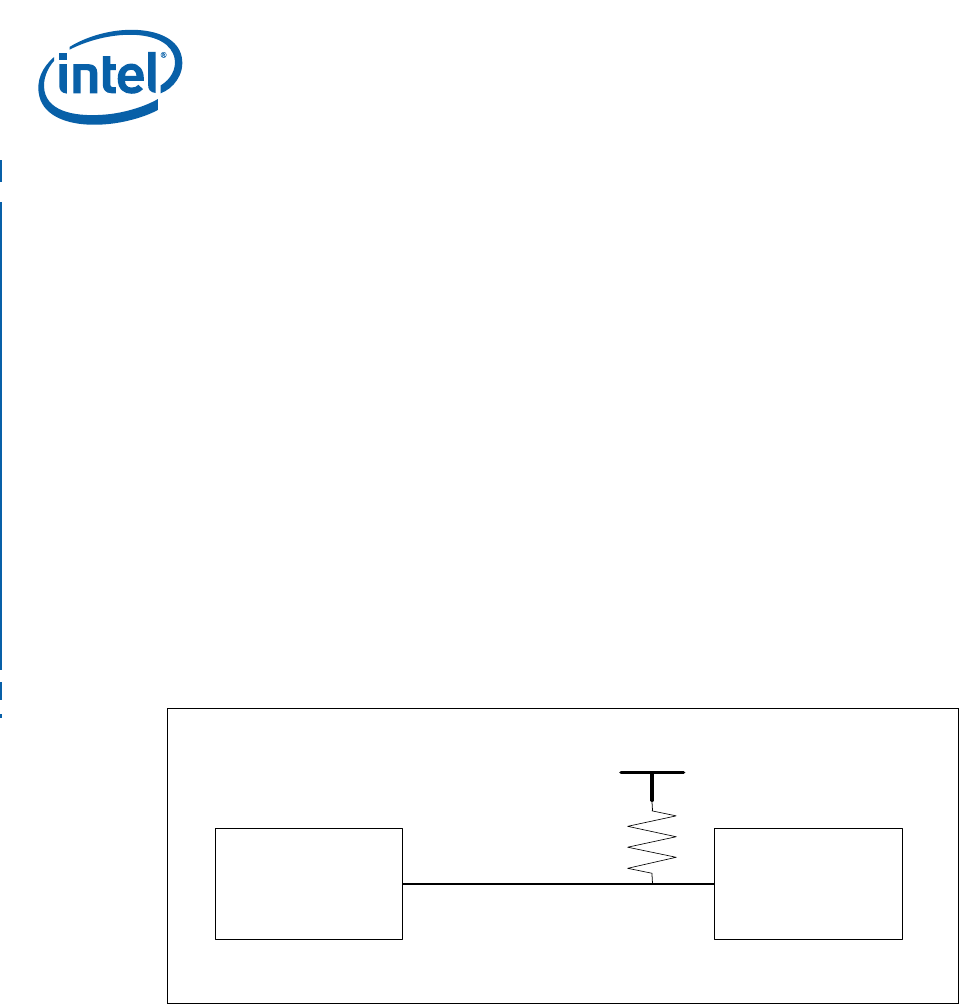
7.1.1 Selecting VTT Power Supply
Selecting the minimum power requirement for VTT supply is a simple calculation that
varies depending on the resistive value of R
VTT terminating resistors. Since all RVTT has
the same value, the power calculation becomes a simple, current times voltage times
the number of terminating resistors used. Figure 30 shows an example of one
terminating network, for which the following equation can be solved for the unknown:
Vout = 0 or 2.5V
VTT=1.25V
R
VTT= 60 Ω (we can assume this value)
N = 73 (from Table 27 obtain the total number of R
VTT resistors)
P = (V x I) x N= (Vout (- or +) VTT) x (VTT/R
VTT) x N
P = (2.5V-1.25V) x (1.25V/60 Ω) x 73
P = 1.9 Watt. Allow a 25% overhead. P = 1.9W + 1.9W x 0.25 = 2.38 Watt
It is very important to allow some overhead for the VTT power supply, just like any
other power distribution allow some overhead in case the value of R
VTT or simply for
inrush current. The following figure shows the diagram of the current paths for the
above equation.
Figure 30. VTT Terminating Circuitry
VTT
IXP46X DDR SDRAM
Vout
R
VTT