Chapter 4
System Architecture Overview
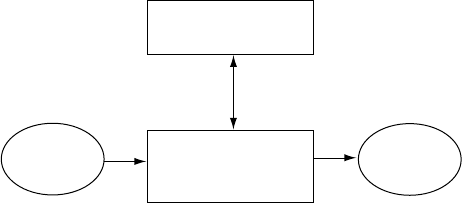
The router architecture consists of two major components:
• Packet Forwarding En gine—Performs Layer 2 and Layer 3 packet switching, route
lookups, and packet forwarding.
• Routing Engine—P rovides Layer 3 routing services and network management.
The Packet F
orwarding Engine and the Routing Engine perform independently but
communicate constantly through a 100-Mbps internal link. This arrangement p rovides
streamlined forwarding and routing control and the ability to run Internet-scale networks at
high speeds
. Figure 12 illustrates the relationship between the Packet Forwarding Engine
and the Routing Engine.
Figure 12: System Architecture
Packet Forwarding
Engine
Routing Engine
1244
Packets
in
Packets
out
100-Mbps link
For a discussion of the architectural components, see the following sections:
• Packet Forwarding Engine Architecture on page 29
• Routing Engine Architecture on page 31
Packet Forwarding Engine Architecture
The Packet Forwarding Engine performs Layer 2 and Layer 3 packet switching. It can forward
up to 40 for all packet sizes. The aggregate throughput for the router is 6.4 gigabits per second
(Gbps), full duplex. The Packet Forwarding Engine is implemented in application-specific
integrated circuits (ASICs). It uses a centralized route lookup engine and shared memory.
The Packet Forwarding Engine architecture includes the following components:
System Architecture Overview
29