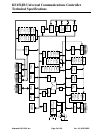
KS152JB Universal Communications Controller
Technical Specifications
Kawasaki LSI USA, Inc. Page 3 of 120 Ver. 0.9 KS152JB2
2.1 Pin Description
Table 1: PIN DESCRIPTION
Name Description
Port 0 Port 0 is an 8-bit open drain bi-directional I/O Port. As an output port each pin can
sink 8 LS TTL inputs. Port 0 pins that have 1s written to them float, and in that
state can be used as high-impedance inputs.
external program memory if EBEN is pulled low. During accesses to external
Data Memory, Port 0 always emits the low-order address byte and serves as the
multiplexed data bus. In these applications it uses strong internal pullups when
emitting 1s.
Port 0 also outputs the code bytes during program verification. External pullups
are required during program verification.
Port 1 Port 1 is an 8 -bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pullups. Port 1 pins that have
1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pullups, and in that state can be
used as inputs. As inputs, Port 1 pins that are externally being pulled low will
source current (I
IL
, on the data sheet) because of the internal pullups.
Port 1 also serves the functions of various special features of the 8XC152, as listed
below:
Pin Name Alternate Function
P1.0 GRXD GSC data input pin
P1.1 GTXD GSC data output pin
P1.2 DEN
GSC enable signal for an external driver
P1.3
TXC GSC input pin for external transmit clock
P1.4
RXC GSC input pin for external receive clock
P1.5 HLD DMA hold input/output
P1.6 HLDA DMA hold acknowledge input/output
Port 2 Port 2 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pullups. Port 2 pins that have
1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pullups, and in that state can be
used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins that are externally being pulled low will
source current (I
IL
, on the data sheet) because of the internal pullups. port 2 emits
the high-order address byte during fetches from external program memory if
EBEN is pulled low. During accesses to external Data Memory that use 16-bit
addresses (MOVX @ DPTR and DMA operations), Port 2 emits the high-order
address byte. In these applications it uses strong internal pullups when emitting
1s. During accesses to external Data Memory that use 8-bit addresses (MOVX @
Ri), Port2 emits the contents of the P2 Special Function Register. Port 2 also
receives the high-order address bits during program verification.