Chapter 6: Technology Background
119
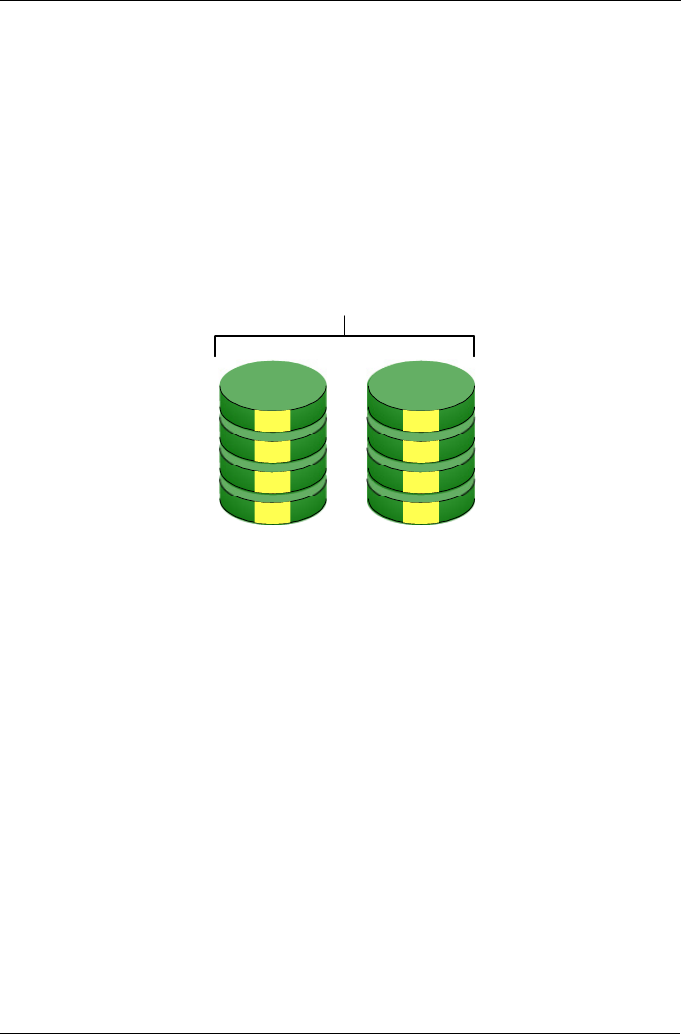
RAID 1 – Mirror
When a RAID Volume is mirrored, identical data is written to a pair of disk drives,
while reads are performed in parallel. The reads are performed using elevator
seek and load balancing techniques where the workload is distributed in the most
efficient manner. Whichever drive is not busy and is positioned closer to the data
will be accessed first.
With RAID 1, if one disk drive fails or has errors, the other mirrored disk drive
continues to function. This is called Fault Tolerance. Moreover, if a spare disk
drive is present, the spare drive will be used as the replacement drive and data
will begin to be mirrored to it from the remaining good drive.
Figure 2. RAID 1 Mirrors identical data to two drives
The RAID Volume’s data capacity equals the smaller disk drive. For example, a
300 GB disk drive and a 500 GB disk drive have a combined capacity of 300 GB
in a mirrored RAID Volume.
If disk drives of different capacities are used, there will also be unused capacity
on the larger drive.
RAID 1 Volumes on SmartStor consist of two disk drives.
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
Data Mirror
disk drives


















