Chapter 4 Hardware and Software Configuration 89
Disk Striping: RAID 0
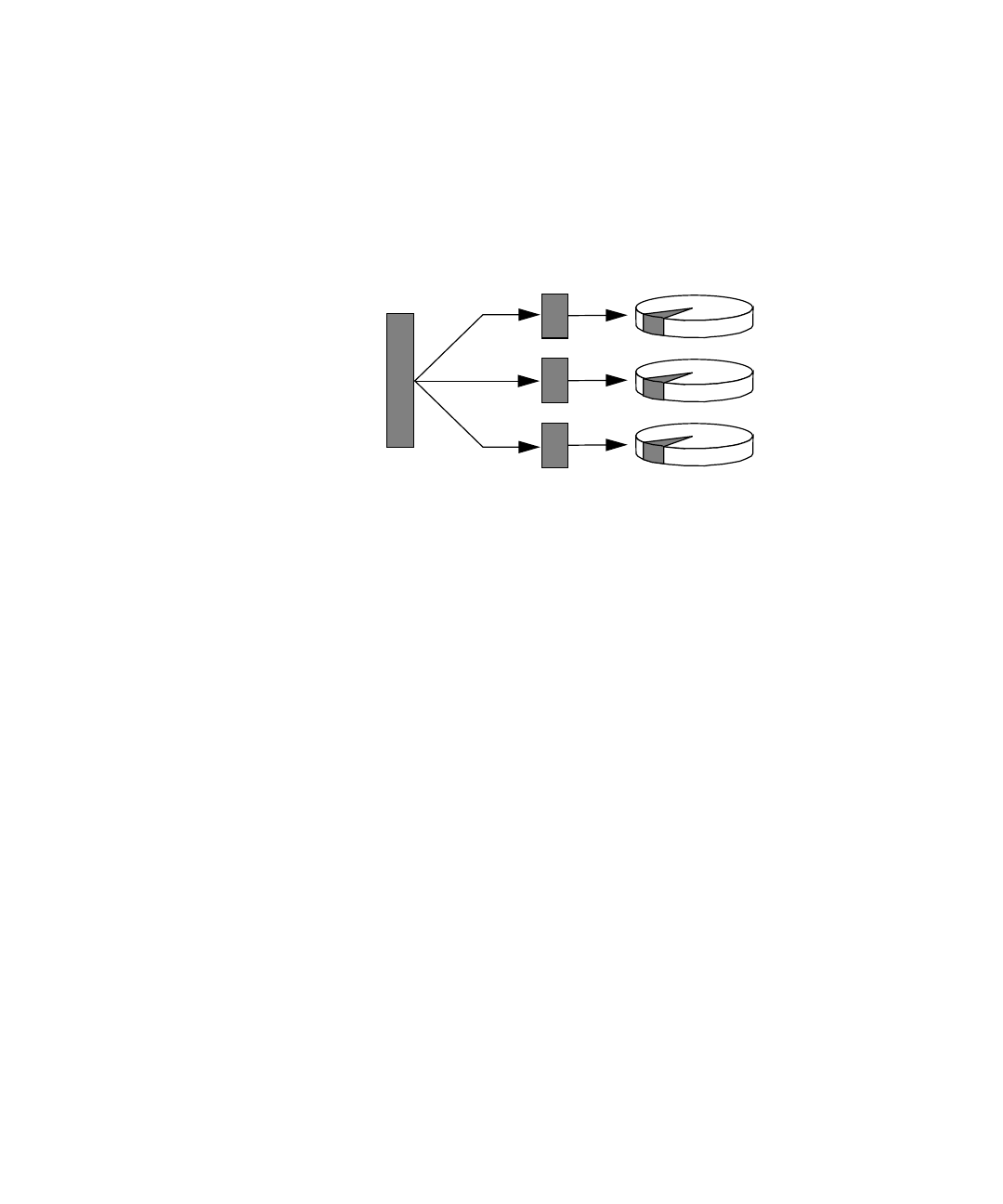
Disk striping (sometimes called RAID 0) is a technique for increasing system
throughput by using several disk drives in parallel. Whereas in non-striped disks the
operating system writes a single block to a single disk, in a striped arrangement each
block is divided and portions of the data are written to different disks.
System performance using RAID 0 will be better than using RAID 1 or 5, but the
possibility of data loss is greater because there is no way to retrieve or reconstruct
data stored on a failed drive.
Disk Striping With Parity: RAID 5
RAID 5 is an implementation of disk striping in which parity information is
included with each disk write. The advantage of the technique is that if any one disk
in a RAID 5 array fails, all the information on the failed drive can be reconstructed
from the data and parity on the remaining disks.
System performance using RAID 5 will fall between that of RAID 0 and RAID 1, but
the system is fully protected from data loss.
Hot Spares
In a hot-spares arrangement, one or more disk drives are installed in the system but
are unused during normal operation. Should one of the active drives fail, disk write
operations are automatically redirected to a hot-spare disk and the failed disk drive
is retired from operation.


















