B
B-4 Color Management
Color conversion
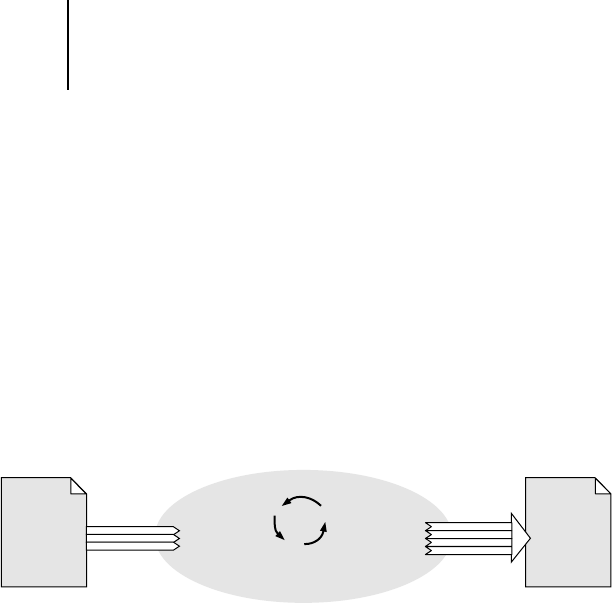
Before a color document can be printed, the color data in it must be
converted to the gamut of the print device. Whether performed by the
iR C2100/2100S or by a host-based CMS, the process of converting color
data for a print device is the same: the CMS interprets RGB image data
according to a specified source profile and adjusts both RGB and CMYK data
according to a specified output profile, also called a destination profile by
some color management systems.
The source profile defines the RGB color space of the image’s source—
characteristics such as the white point, gamma, and type of phosphors used.
The output profile defines the gamut of the output device. The iR C2100/
2100S (or the host-based CMS) uses a device-independent color space to
translate between the source color space and the color space of the output
device.
The iR C2100/2100S allows you to specify default and override settings for
the source color space information and the output profile information (see
page 1-1). When you use these settings, you do not need to use the features of
other color management systems. Your iR C2100/2100S software includes
ICC profiles for use with other color management systems, if you choose to
use them, although conflicts may arise when the iR C2100/2100S CMS is
used in conjunction with a host CMS.
Color management systems can also be used to adjust color data to the gamut
of a print device other than the one to which you are printing. This process of
simulating another print device is commonly used for proofing jobs that will
print on an offset press. The iR C2100/2100S simulation feature is described
on page 1-7.
Input data Printed data or file
Color management sy
stem
Device-independent
color space
Source
profile
Output
profile


















