DBC Network Bridge
Operation Manual page 57
5.3.3 Input Gate
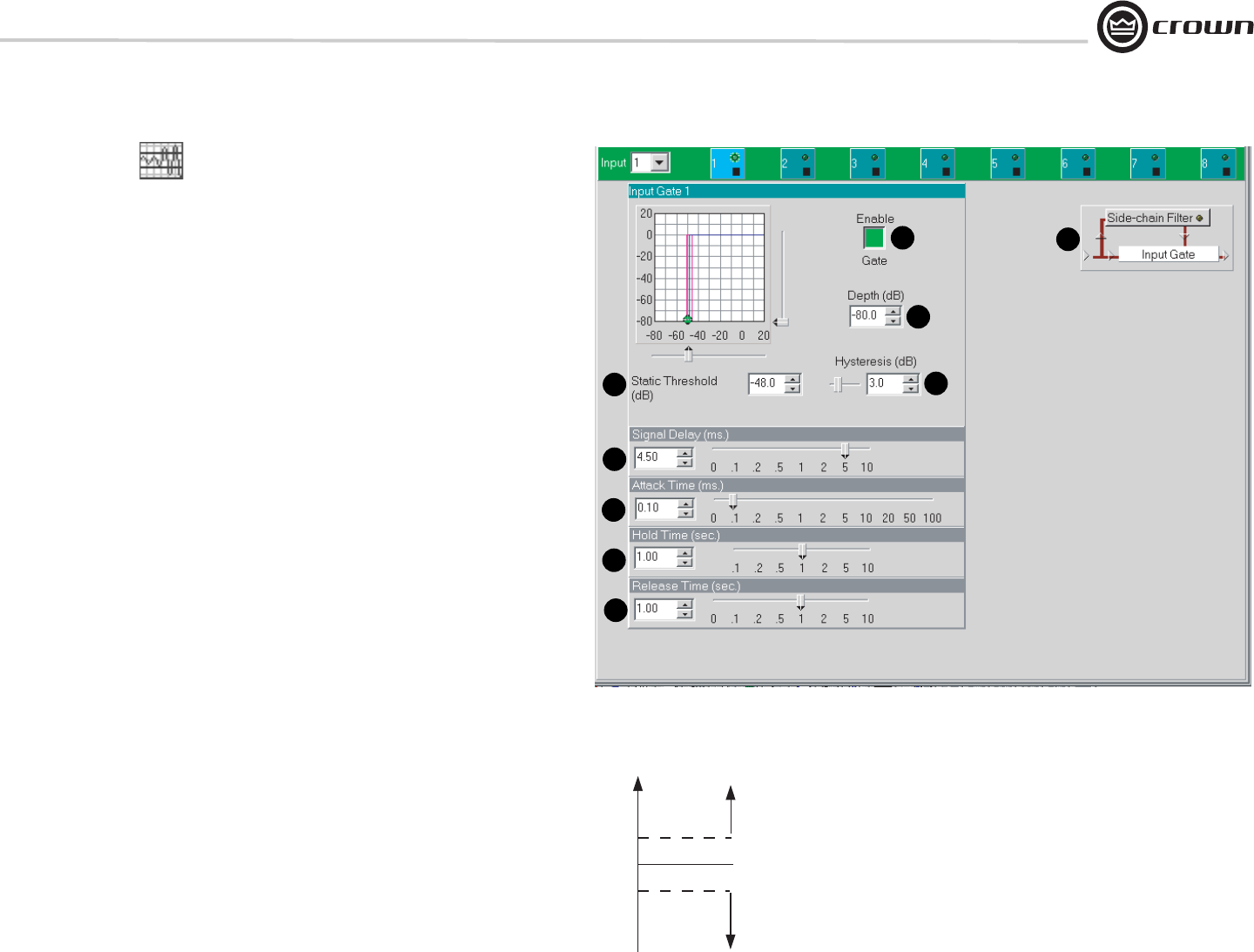
Starting from the Input Path window, you can access the Input Gate window (Figure 5.20) by clicking on its icon
(shown above). The Input Gate feature allows signals above a certain level to pass and attenuates lower level signals.
When 'open', the Input Gate passes the input signal un-attenuated. When 'closed', it attenuates the input signal by an
amount specified with the Depth control. There are eight parameters which control this feature:
1. Enable Gate
Switches the gate on or off.
2. Depth
Sets the 'closed' gain of the Gate. Control range is from –100 dB to 0 dB in 0.5 dB steps.
3. Static Threshold
Specifies the peak signal level (after side-chain processing) above which the gate will open. Control range is from –80
to +20 dB in 0.5 dB steps.
4. Hysteresis
Sets a range in dB above and below the Threshold which separates the levels at which the Input Gate opens and closes
(Figure 5.21). The input signal must reach a level above the Threshold plus Hysteresis to open. Once opened, the
input must reach a level below the Threshold minus Hysteresis to close. Control range is from 0 dB to 12 dB in 0.5 dB
steps.
5. Signal Delay
Additional delay applied to the input signal, but not to the control key signal. Provided to allow the Input Gate to 'look
ahead' in time. Control range is from 0 milliseconds to 10 milliseconds.
6. Attack Time
Sets the time required for the Input Gate to increase its gain by 20 dB. Control range is from 0.2 millisecond to 100
milliseconds.
7. Hold Time
Determines how long the Input Gate will remain open after the control key signal falls below the Threshold. Control
range is from 0.01 second to 10 seconds.
8. Release Time
Sets the time required for the Input Gate to decrease its gain by 20 dB. Control range is from 0.01 second to 10 sec-
ond.
9. Side-chain Filter
The Side-chain Filter processes the Control Key signal used to trigger the Input Gate. Its output is not directly in the
signal path, and only affects the sensitivity of the Gate Threshold versus frequency. This filter can be especially useful
in situations where certain frequency components need to be rejected by the gate. The use of this filter in conjunction
with the Signal Delay can provide de-essing of the gate.
5 Advanced Operation
Figure 5.20 Input Gate Window
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Input Level
Open
Threshold
Close
Figure 5.21 Hysteresis