Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600/E5-2600/E5-4600 Product Families 185
Datasheet Volume One
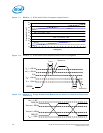
7.9.5.2 Overshoot/Undershoot Pulse Duration
Overshoot/undershoot pulse duration describes the total amount of time that an
overshoot/undershoot event exceeds the overshoot/undershoot reference voltage. The
total time could encompass several oscillations above the reference voltage. Multiple
overshoot/undershoot pulses within a single overshoot/undershoot event may need to
be measured to determine the total pulse duration.
Note: Oscillations below the reference voltage cannot be subtracted from the total overshoot/
undershoot pulse duration.
7.9.5.3 Activity Factor
Activity factor (AF) describes the frequency of overshoot (or undershoot) occurrence
relative to a clock. Since the highest frequency of assertion of any common clock signal
is every other clock, an AF = 0.1 indicates that the specific overshoot (or undershoot)
waveform occurs every other clock cycle.
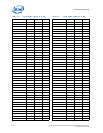
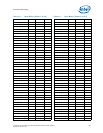
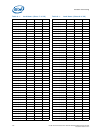
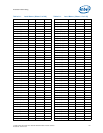
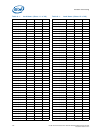
The specification provided in the table shows the maximum pulse duration allowed for a
given overshoot/undershoot magnitude at a specific activity factor. Each table entry is
independent of all others, meaning that the pulse duration reflects the existence of
overshoot/undershoot events of that magnitude ONLY. A platform with an overshoot/
undershoot that just meets the pulse duration for a specific magnitude where the AF <
0.1, means that there can be no other overshoot/undershoot events, even of lesser
magnitude (note that if AF = 0.1, then the event occurs at all times and no other
events can occur).
7.9.5.4 Reading Overshoot/Undershoot Specification Tables
The overshoot/undershoot specification for the processor is not a simple single value.
Instead, many factors are needed to determine the over/undershoot specification. In
addition to the magnitude of the overshoot, the following parameters must also be
known: the width of the overshoot and the activity factor (AF). To determine the
allowed overshoot for a particular overshoot event, the following must be done:
1. Determine the signal group a particular signal falls into.
2. Determine the magnitude of the overshoot or the undershoot (relative to VSS).
3. Determine the activity factor (How often does this overshoot occur?).
4. Next, from the appropriate specification table, determine the maximum pulse
duration (in nanoseconds) allowed.
5. Compare the specified maximum pulse duration to the signal being measured. If
the pulse duration measured is less than the pulse duration shown in the table,
then the signal meets the specifications.
Undershoot events must be analyzed separately from overshoot events as they are
mutually exclusive.
7.9.5.5 Determining if a System Meets the Overshoot/Undershoot
Specifications
The overshoot/undershoot specifications listed in the table specify the allowable
overshoot/undershoot for a single overshoot/undershoot event. However most systems
will have multiple overshoot and/or undershoot events that each have their own set of
parameters (duration, AF and magnitude). While each overshoot on its own may meet