Register-Level Programming Chapter 4
PC-DIO-96 User Manual 4-14 © National Instruments Corporation
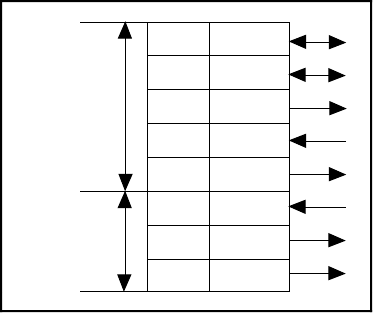
At the digital I/O connector, port C has the following pin assignments when in mode 1 input.
Notice that the status of STBA* and the status of STBB* are not included in the port C status
word.
PC7
PC6
PC5
PC4
PC3
PC2
PC1
PC0
I/O
I/O
IBFA
STBA*
INTRA
STBB*
IBFB
INTRB
Group A
Group B
Mode 1 Input Programming Example
The following example shows how to configure PPI A for various combinations of mode 1 input.
This code is strictly an example and is not intended to be used without modification in a practical
situation.
Main() {
#define BASE_ADDRESS 0x180 /* Board located at address 180 */
#define APORTAoffset 0x00 /* Offset for PPI A, port A */
#define APORTBoffset 0x01 /* Offset for PPI A, port B */
#define APORTCoffset 0x02 /* Offset for PPI A, port C */
#define ACNFGoffset 0x03 /* Offset for PPI A, CNFG */
unsigned int porta, portb, portc, cnfg;
char valread; /* Variable to store data read from a
port */
/* Calculate register addresses */
porta = BASE_ADDRESS + APORTAoffset;
portb = BASE_ADDRESS + APORTBoffset;
portc = BASE_ADDRESS + APORTCoffset;
cnfg = BASE_ADDRESS + ACNFGoffset;
/* EXAMPLE 1–port A input */
outp(cnfg,0xB0); /* Port A is an input in mode 1. */
while (!(inp(portc) & 0x20)); /* Wait until IBFA is set, indicating that
data has been loaded in port A. */
valread = inp(porta); /* Read the data from port A. */
/* EXAMPLE 2–Port B input */
outp(cnfg,0x86); /* Port B is an input in mode 1. */
while (!(inp(portc) & 0x02)); /* Wait until IBFB is set, indicating that
data has been loaded in port B. */
valread = inp(portb);
}