Web OS 10.0 Application Guide
Chapter 10: Health Checking
227
212777-A, February 2002
Scripting Guidelines
n Use generic result codes that are standard and defined by the RFC, as applicable. This
helps ensure that if the customer changes server software, the servers won’t start failing
unexpectedly.
n Search only for the smallest and most concise piece of information possible. Each script
cannot exceed 1K in size, so use the space wisely.
n Avoid tasks that may take a long time to perform or the health check will fail. For exam-
ple, avoid tasks that exceed the interval for load balancing.
Script Configuration Examples
Script Example 1: A Basic Health Check
Configure the switch to check a series of Web pages (HTML or dynamic CGI scripts) before it
declares a real server is available to receive requests.
NOTE – If you are using the CLI to create a health check script, you must use quotes (“) to
indicate the beginning and end of each command string.
NOTE – When you are using the command line interface to enter the send string as an argu-
ment to the send command, you must type two “\”s before an “n” or “r.” If you are instead
prompted for the line, that is, the text string is entered after hitting <return>, then only one “\”
is needed before the “n” or “r.”
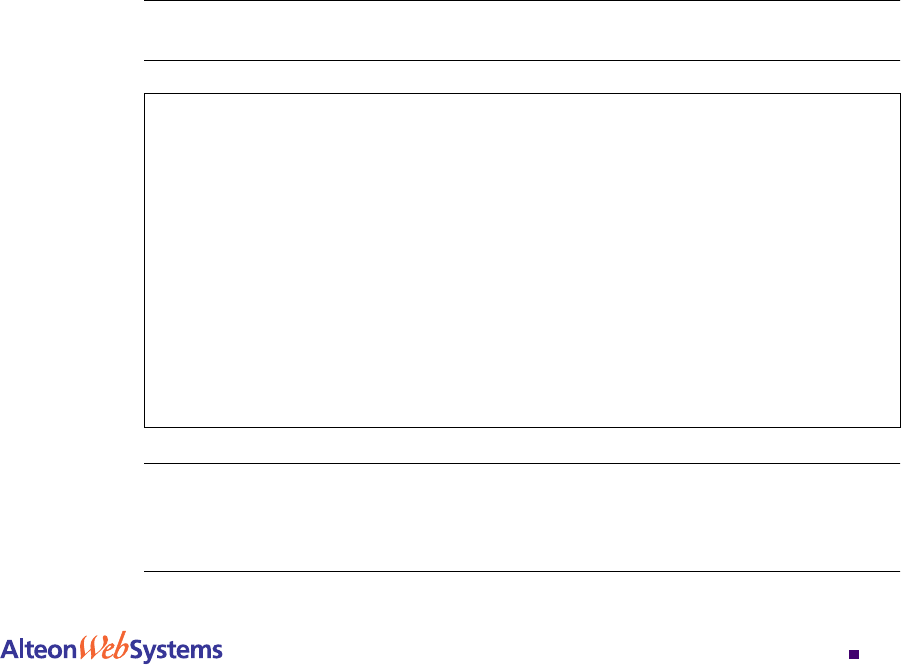
/cfg/slb/group x/health script1/content none
/cfg/slb/adv/script1
open
80
send
"GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
\\r\\n
HOST:www.hostname.com\\r\\n\\r\\n"
expect
"HTTP/1.1 200"
close
open
80
send
"GET /script.cgi HTTP/1.1
\\r\\n
HOST:www.hostname.com\\r\\n\\r\\n"
expect
"HTTP/1.1 200"
close
open
443
…
close


















