Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 78 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
8.5 Oscillation Stop and Re-oscillation Detection Function
The oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function is such that main clock oscillation circuit stop and
re-oscillation are detected. At oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection, reset or oscillation stop, re-oscillation
detection interrupt request are generated. Which one is to be generated can be selected using the CM27 bit
in the CM2 register.
The oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function can be enabled or disabled using the CM20 bit in
the CM2 register.
Table 8.9 lists a specification overview of the oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function.
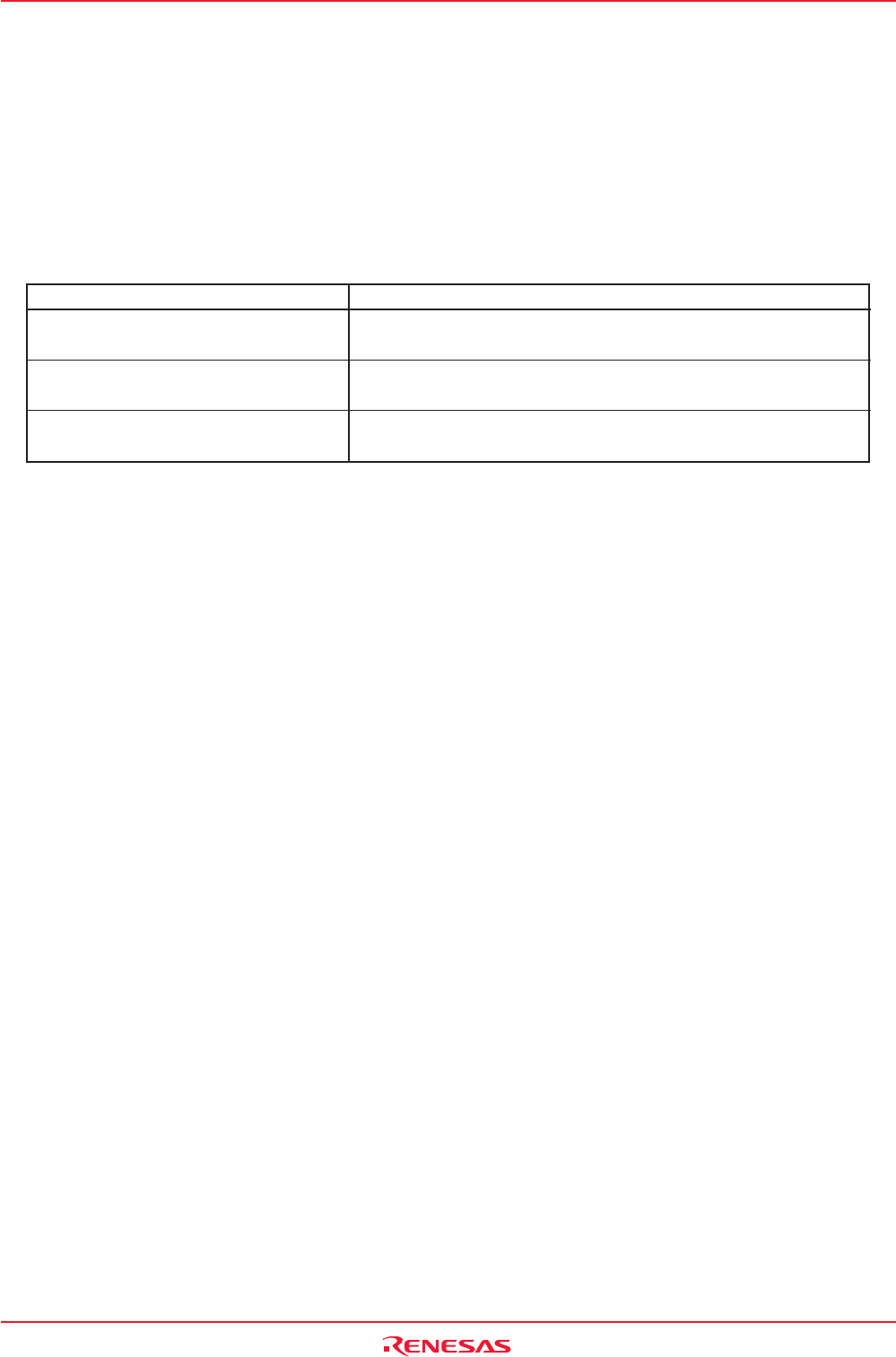
Table 8.9 Specification Overview of Oscillation Stop and Re-oscillation Detection Function
Item Specification
Oscillation Stop Detectable Clock and f(XIN) ≥ 2 MHz
Frequency Bandwidth
Enabling Condition for Oscillation Stop Set CM20 bit to “1” (enable)
and Re-oscillation Detection Function
Operation at Oscillation Stop, •Reset occurs (when CM27 bit = 0)
Re-oscillation Detection •
Oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt occurs (when the CM27 bit =1)
8.5.1 Operation When CM27 Bit = 0 (Oscillation Stop Detection Reset)
Where main clock stop is detected when the CM20 bit is “1” (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection
function enabled), the microcomputer is initialized, coming to a halt (oscillation stop reset; refer to
4. Special Function Register (SFR), 5. Reset).
This status is reset with hardware reset. Also, even when re-oscillation is detected, the microcomputer
can be initialized and stopped; it is, however, necessary to avoid such usage (During main clock stop, do
not set the CM20 bit to “1” and the CM27 bit to “0”).
8.5.2 Operation When CM27 Bit = 1 (Oscillation Stop, Re-oscillation Detection Interrupt)
Where the main clock corresponds to the CPU clock source and the CM20 bit is “1” (oscillation stop, re-oscillation
detection function enabled), the system is placed in the following state if the main clock comes to a halt:
• Oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt request is generated.
• The on-chip oscillator starts oscillation, and the on-chip oscillator clock becomes the clock source for
CPU clock and peripheral functions in place of the main clock.
• CM21 bit = 1 (on-chip oscillator clock is the clock source for CPU clock)
• CM22 bit = 1 (main clock stop detected)
• CM23 bit = 1 (main clock stopped)
Where the PLL clock corresponds to the CPU clock source and the CM20 bit is “1”, the system is placed
in the following state if the main clock comes to a halt: Since the CM21 bit remains unchanged, set it to “1”
(on-chip oscillator clock) inside the interrupt routine.
• Oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt request is generated.
• CM22 bit = 1 (main clock stop detected)
• CM23 bit = 1 (main clock stopped)
• CM21 bit remains unchanged
Where the CM20 bit is “1”, the system is placed in the following state if the main clock re-oscillates from
the stop condition:
• Oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt request is generated.
• CM22 bit = 1 (main clock re-oscillation detected)
• CM23 bit = 0 (main clock oscillation)
• CM21 bit remains unchanged


















