79
D14049.04
JULY 2008
Grey Headline (continued)
TANDBERG VIDEO COMMUNICATIONS SERVER
ADMINISTRATOR GUIDE
Introduction Getting Started
Overview and
Status
System
Conguration
VCS
Conguration
Zones and
Neighbors
Call
Processing
Bandwidth
Control
Firewall
Traversal
Appendices
Applications Maintenance
Registration Control
About Alias Registration
Once the authentication process (if required) has been
completed, the endpoint will then attempt to register its alias(es)
with the VCS.
H.323
An H.323 endpoint may attempt to register with the VCS using an alias that has already been registered on the VCS from another IP
address. The reasons for this could include:
two endpoints at different IP addresses are attempting to register using the same alias
•
a single endpoint has previously registered using a particular alias. The IP address allocated to the endpoint, or the port the
•
endpoint uses to communicate with the VCS, then changes, and the endpoint is attempting to re-register using the same alias.
You can determine how the VCS will behave in this situation by conguring the Registration Conict Mode.
Registering Aliases
SIP
A SIP endpoint will always be allowed to register using an alias
that is already in use from another IP address. When a call is
received for this alias, all endpoints registered using that alias
will be called simultaneously. This SIP feature is known as
“forking”.
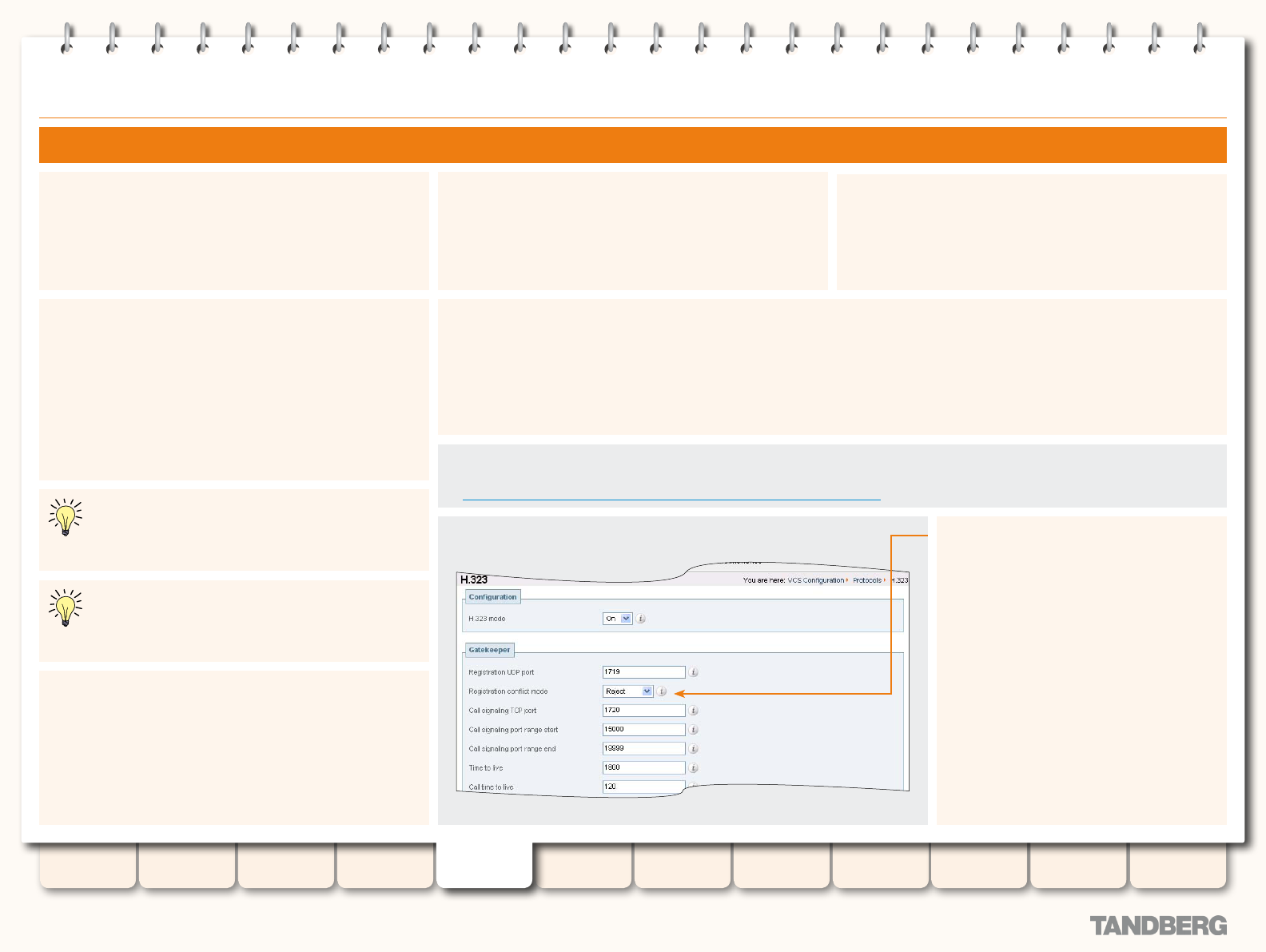
Registration conict mode
Determines what will happen when an H.323
endpoint attempts to register using an alias
that has already been registered from another
IP address.
Reject: The registration from the new IP
address will be rejected. This is useful if your
priority is to prevent two users registering with
the same alias.
Overwrite: The existing registration will be
overwritten using the new IP address. This is
useful if your network is such that endpoints
are often allocated new IP addresses, because
it will prevent unwanted registration rejections.
The default is Reject.
SIP Alias Registration
When registering, the SIP endpoint presents the VCS with its
contact address (IP address) and logical address (Address of
Record). The logical address is considered to be its alias, and
will generally be in the form of a URI.
H.323 Alias Registration
When registering, the H.323 endpoint presents the VCS with one
or more of the following:
one or more H.323 IDs
•
one or more E.164 aliases
•
one or more URIs.
•
Users of other registered endpoints can then call the endpoint
by dialing any of these aliases.
We recommended that you do not use aliases that reveal
sensitive information. Due to the nature of H.323, call
setup information is exchanged in an unencrypted form.
Attempts to Register using an Existing Alias
An endpoint may attempt to register with the VCS using an alias
that is already registered to the system. How this is managed
depends on how the VCS is congured and whether the endpoint
is SIP or H.323.
We recommended that you register your H.323 endpoints
using a URI. This facilitates interworking between SIP
and H.323, as SIP endpoints register using a URI as
standard.
To conguring the Registration Conict Mode:
VCS Conguration > Protocols > H.323
•
. You will be taken to the H.323 page.
xConguration H323 Gatekeeper Registration ConictMod
•
e