MS860 WiFi Manual
SCANNER CONFIGURATION MANAGER
36
Parity
Parity is an archaic technique used to detect data transmission errors by
adding an extra bit to each character. This scheme has been sup-
planted in modern communication devices by “Error Correction”.
Default (and the current universal standard) is “No Parity”.
The RS232 input characteristics of the MS860 can be modified accord-
ing to the following nine parameters:
RS232
Baud Rate
Baud Rate (bits per second) refers to the speed of the data from the
MS860. Normally, the baud rate of the host RS232 port should match
that of the input device.
Default is “9600 Baud”.
Data bit refers to the number of bits per byte that are dedicated to data
(minus start/stop bits).
Default (and the current universal standard) is “8 Data Bits”.
Data Bit
Handshaking
Handshaking is the mechanism that controls the speed of data flow so
that a slower receiver of data is not overwhelmed by a faster sender of
data. Selections are:
Ignore
RTS (request to send)
Enabled at Power Up
RTS Enabled in Communication
Default is “Ignore”.
ACK/NAK
Data characters that are sent from the receiver to the sender in order
to “acknowlege” or “not acknowlege” the receipt of the data without
error. Rarely used these days.
Default (and the current universal standard) is “No”.
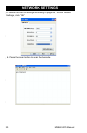
Step 5: Select DHCP on or off. Click “Yes” for DHCP on and click
“No” for DHCP off.
Step 6: If select DHCP “off”, fill in IP address, Subnet Mask and
Gateway, click on “NEXT” button