DI-1162/DI-1162M Remote Access Router
79
The parameters are described as follows:
♦
Global IP
– This is a single, global IP Address that is valid on the Internet, or on the same subnet of the global
interface.
♦
Local IP
– This is a single, local IP Address that is not valid on the Internet.
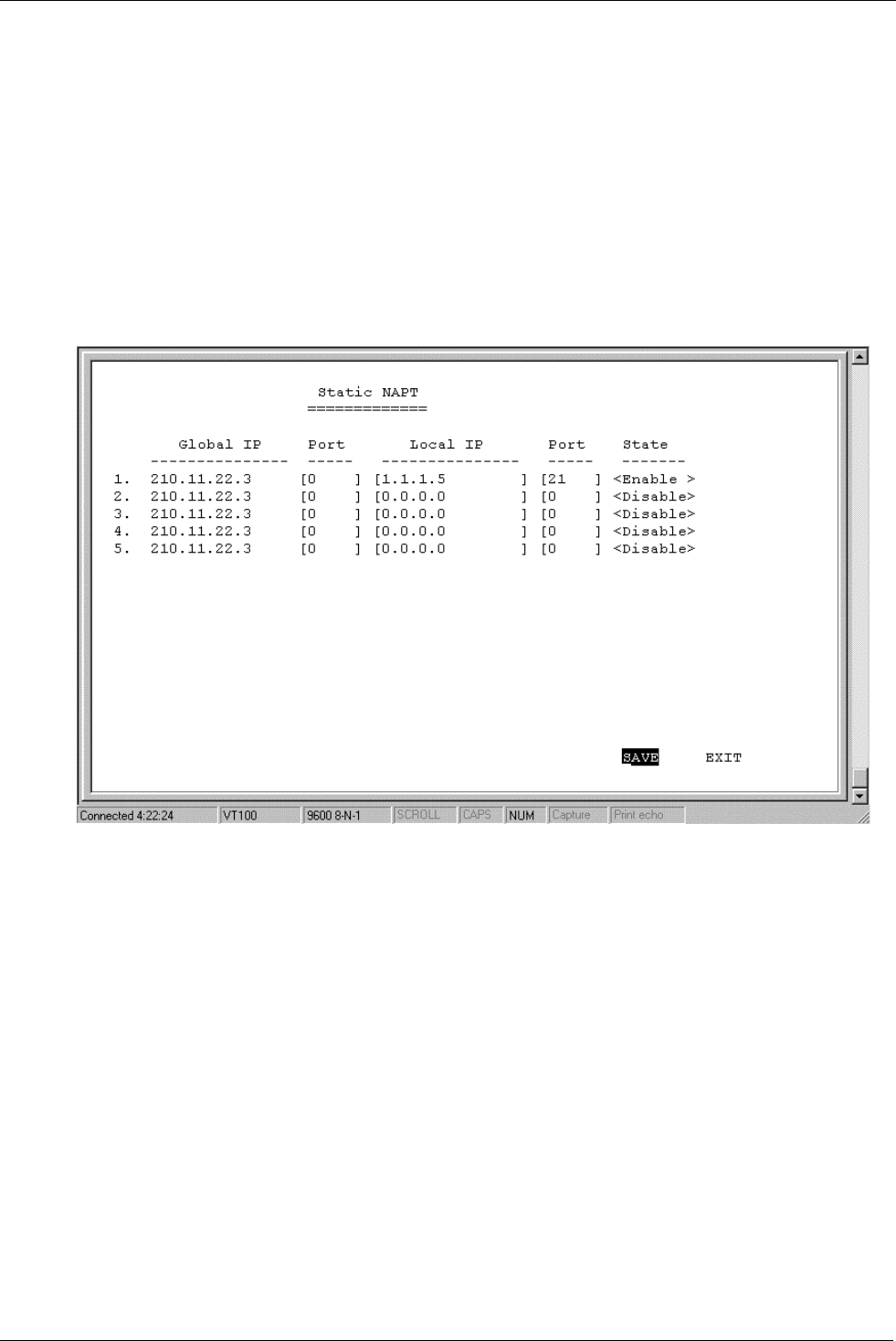
Static NAPT
This screen (below) is how the
NAT IP Pool
appears, if
Static NAPT
was chosen for the
Translation Mode
parameter. Each entry in this configuration can be used to map a global address and port to a local address and
port. Notice that the global address will be the external IP address of the global interface.
♦
Port –
This is a destination port number, used by TCP and UDP, to de-multiplex the incoming IP packet.
In the above example, incoming packets with the global destination IP Address (211.11.22.2) and global
destination TCP/UDP port (21) will be translated to a packet with the local destination IP Address (1.1.1.5) and
local TCP/UDP port (21).
Port 21 is assigned to FTP servers. Please see
“Appendix D”
for more commonly assigned port numbers, or RFC
1700 for a more complete list.
NAPT for Special Aps
Some applications programs that are used over the Internet such as Microsoft NetMeeting, Diablo, and CU See Me
send information to a certain port number or within a specified range of port numbers. The exact port number used
is specific to the application. However, if you find that you are having trouble using an application over the
Internet and you are using NAPT, you may need to exempt certain port numbers from the NAPT port translation
process. Please refer to the user guide for the program to find out whether it transmits and receives data only
through specified IP port numbers. In order for these programs to work with NAPT, the IP port numbers required
by these applications must be entered in the Configure NAPT for Special APs screen shown below.


















