104
Enhancements in Release F.04.08
Configuring RADIUS Authentication and Accounting
Switch Operating Rules for RADIUS
■ You must have at least one RADIUS server accessible to the switch.
■ The switch supports authentication and accounting using up to three RADIUS servers. The
switch accesses the servers in the order in which they are listed by the show radius command
( page 121). If the first server does not respond, the switch tries the next one, and so-on. (To
change the order in which the switch accesses RADIUS servers, refer to “Changing RADIUS-
Server Access Order” on page 126.)
■ You can select RADIUS as the primary authentication method for each type of access. (Only
one primary and one secondary access method is allowed for each access type.)
■ In the Series 2500 switches, EAP RADIUS uses MD5 and TLS to encrypt a response to a
challenge from a RADIUS server.
General RADIUS Setup Procedure
Preparation:
1. Configure one to three RADIUS servers to support the switch. (That is, one primary server and
one or two backups.) Refer to the documentation provided with the RADIUS server application.
2. Before beginning to configure the switch, collect the information outlined below.
Table 8. Preparation for Configuring RADIUS on the Switch
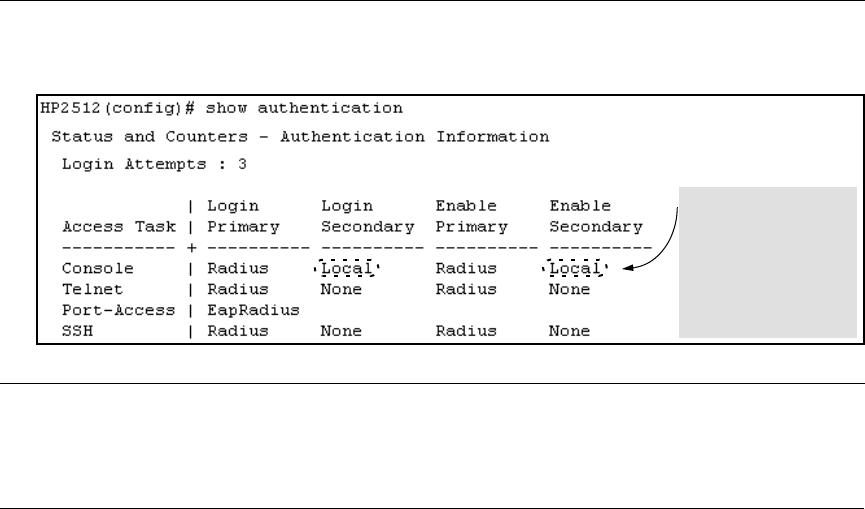
• Determine the access methods (console, Telnet, Port-Access, and/or SSH) for which you want RADIUS as the primary
authentication method. Consider both Operator (login) and Manager (enable) levels, as well as which secondary
authentication methods to use (local or none) if the RADIUS authentication fails or does not respond.
Figure 41. Example of Possible RADIUS Access Assignments
• Determine the IP address(es) of the RADIUS server(s) you want to support the switch. (You can configure the switch
for up to three RADIUS servers.)
Console access requires
Local as secondary
method to prevent lockout
if the primary RADIUS
access fails due to loss of
RADIUS server access or
other problems with the
server.


















