Accessing DB2 Data from the Web Using Java
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and Embedded SQL for Java (SQLJ) are
provided with DB2 to allow you to create applications that access data in DB2
databases from the Web.
Programming languages containing embedded SQL are called host languages.
Java differs from the traditional host languages C, COBOL, and FORTRAN, in
ways that significantly affect how it embeds SQL:
v SQLJ and JDBC are open standards, enabling you to easily port SQLJ or
JDBC applications from other standards-compliant database systems to DB2
Universal Database.
v All Java types representing composite data, and data of varying sizes, have
a distinguished value, null, which can be used to represent the SQL NULL
state, giving Java programs an alternative to NULL indicators that are a
fixture of other host languages.
v Java is designed to support programs that, by nature, are heterogeneously
portable (also called ″super portable″ or simply ″downloadable″). Along
with Java’s type system of classes and interfaces, this feature enables
component software. In particular, an SQLJ translator written in Java can
call components that are specialized by database vendors in order to
leverage existing database functions such as authorization, schema
checking, type checking, transactional, and recovery capabilities, and to
generate code optimized for specific databases.
v Java is designed for binary portability in heterogeneous networks, which
promises to enable binary portability for database applications that use
static SQL.
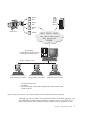
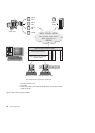
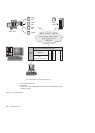
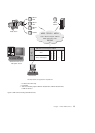
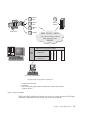
v You can run JDBC applets inside a web page on any system with a
Java-enabled browser, regardless of the platform of your client. Your client
system requires no additional software beyond this browser. The client and
the server share the processing of JDBC and SQLJ applets and applications.
The JDBC server and the DB2 client must reside on the same machine as the
Web server. The JDBC server calls the DB2 client to connect to local, remote,
host, and AS/400 databases. When the applet requests a connection to a DB2
database, the JDBC client opens a TCP/IP connection to the JDBC server on
the machine where the Web server is running.
14 Quick Beginnings