MultiProcessor Specification
3-14 Version 1.4
REG.
MARK
I/O APIC
1
8259A-
EQUIVALENT
PICS
NON-ISA INTERRUPT
INTERRUPT
ROUTING
NETWORK
I/O APIC
2
ICC BUS
INTR/LINT0
ISA INTERRUPT
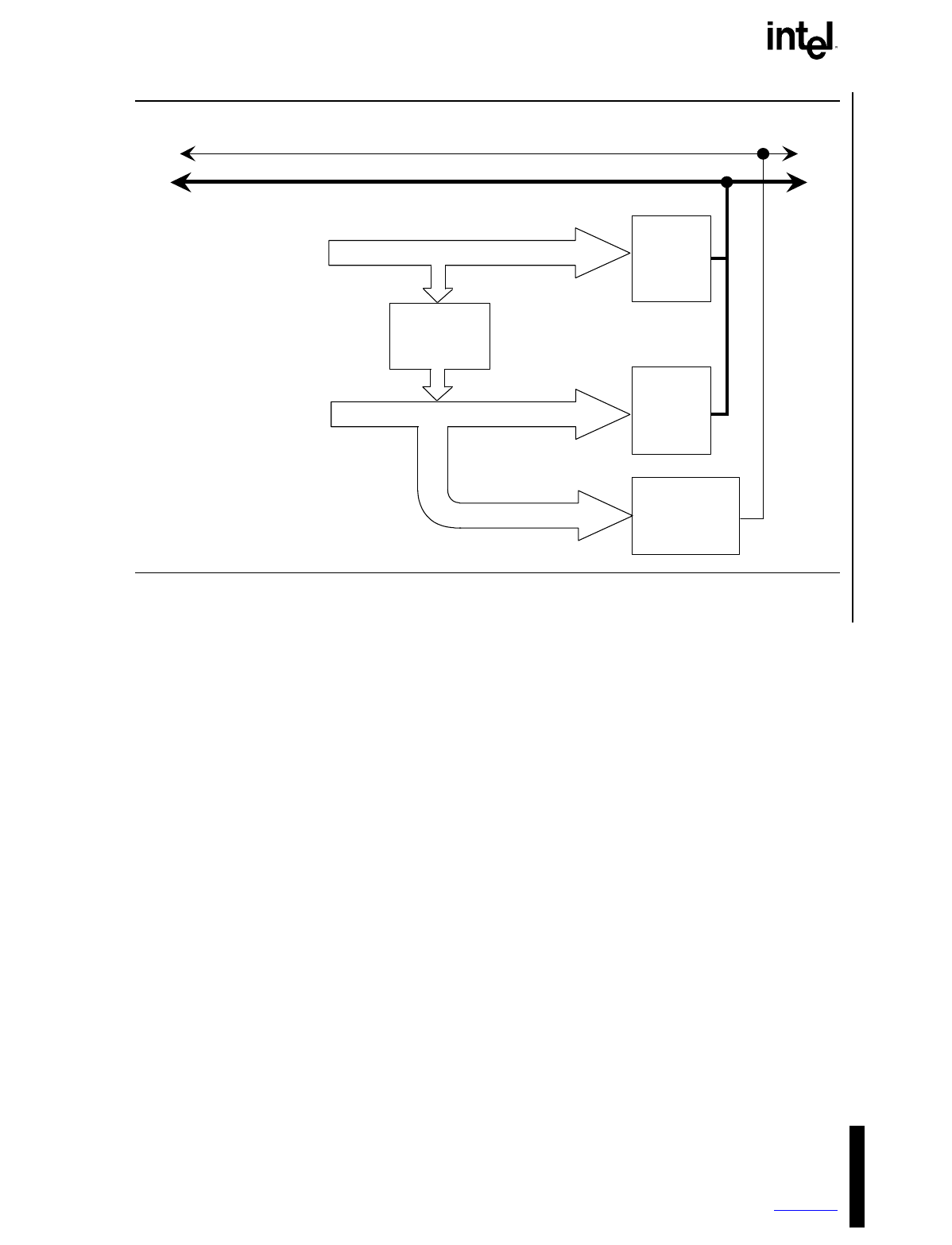
Figure 3-6. Multiple I/O APIC Configurations
3.7 RESET Support
To bring all circuitry in a computer system to an initial state, computer systems require a system-
wide reset capability. To support multiple processors, a compliant system requires a processor-
specific reset or initialization capability in addition to the typical system-wide reset and
initialization capabilities.
• The term “RESET” refers to the system-wide hard reset. It refers to the RESET signal on both
Pentium and Intel486 processors or the RESET signal of the 82489DX APIC. (See
Section 3.7.1.)
• The term “INIT,” refers to either a system-wide soft reset/initialization or a processor-specific
initialization. For example, the term “INIT” may refer to the INIT signal on the Pentium
processor or to the RESET signal on the Intel486 processor. (See Sections 3.7.2. and 3.7.3.)
Because the INIT signal is available on the Pentium processor but not on the Intel486 processor,
the remainder of this document uses the above-mentioned special definitions for the terms “INIT”
and “RESET”:
3.7.1 System-wide RESET
The system-wide RESET, as defined by this specification, refers to a hard or cold reset, which
sets all circuitry, including processor, coprocessor, add-in cards, and control logic, to an initial
state. A hard reset is the reset signal that is sent to all components of the system during a power-on


















