MP Configuration Table
Version 1.4 4-3
4.1 MP Floating Pointer Structure
An MP-compliant system must implement the MP floating pointer structure, which is a variable
length data structure in multiples of 16 bytes. Currently, only one 16-byte data structure is defined.
It must span a minimum of 16 contiguous bytes, beginning on a 16-byte boundary, and it must be
located within the physical address as specified in the previous section. To determine whether the
system conforms to the MP specification, the operating system must search for the MP floating
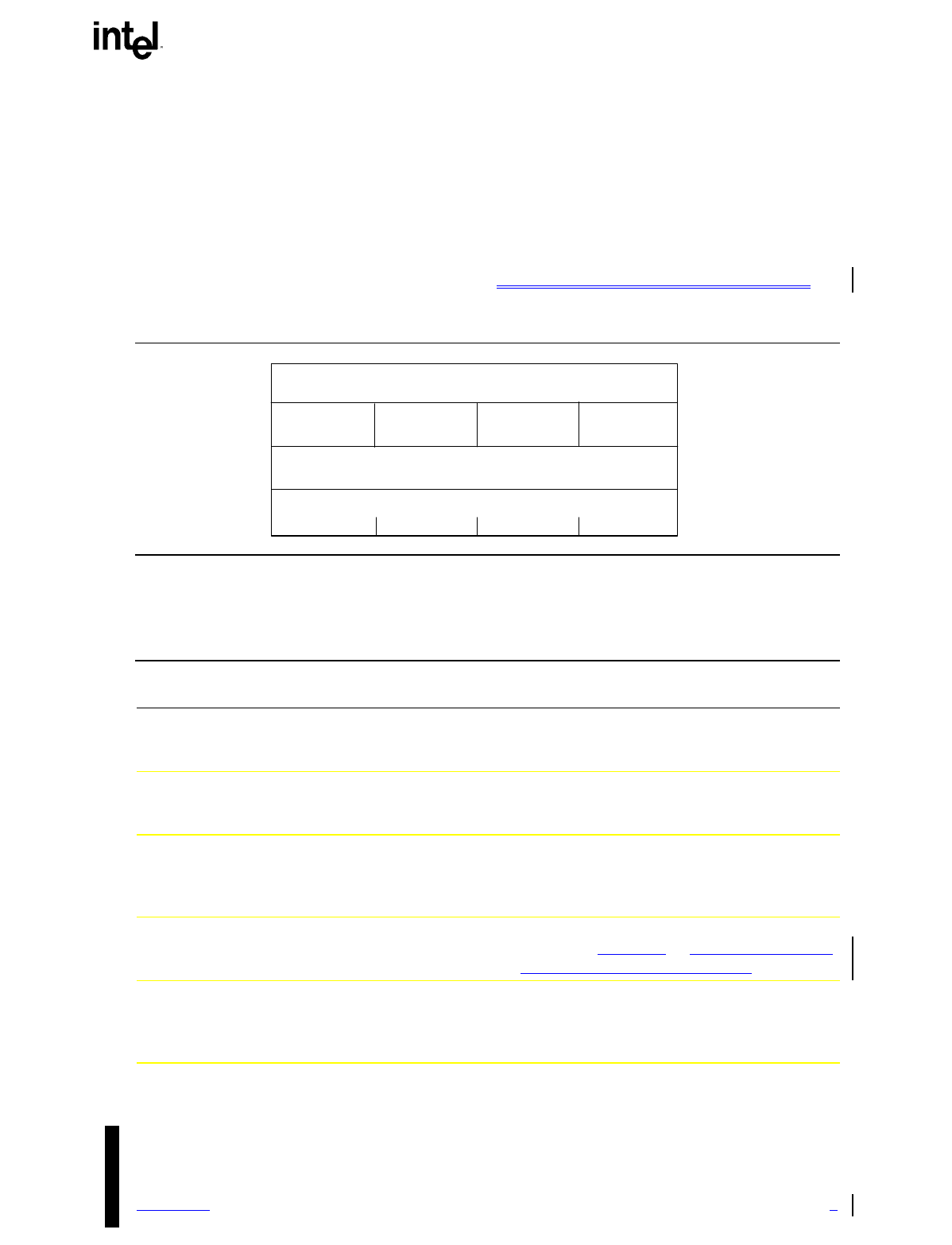
pointer structure in the order specified in the previous section. Figure 4-2 shows the format of this
structure, and Table 4-1 explains each of the fields. See also Appendix E, for more information.
SPEC_REV
LENGTH
_ (5Fh)M (4Dh)
SIGNATURE
00H
04H
CHECKSUM
08
0CH
H
31 07815162324
31 07815162324
PHYSICAL ADDRESS POINTER
P (50h)_ (5Fh)
MP FEATURE
BYTE 1
MP FEATURE
BYTES 2-5
Figure 4-2. MP Floating Pointer Structure
Table 4-1. MP Floating Pointer Structure Fields
Field
Offset
(in bytes:bits)
Length
(in bits) Description
SIGNATURE 0 32 The ASCII string represented by “_MP_” which
serves as a search key for locating the pointer
structure.
PHYSICAL ADDRESS
POINTER
4 32 The address of the beginning of the MP
configuration table. All zeros if the MP
configuration table does not exist.
LENGTH 8 8 The length of the floating pointer structure table
in paragraph (16-byte) units. The structure is
16 bytes or 1 paragraph long; so this field
contains 01h.
SPEC_REV 9 8 The version number of the MP specification
supported. A value of 01h indicates Version 1.1.
A value of 04h indicates Version 1.4.
CHECKSUM 10 8 A checksum of the complete pointer structure.
All bytes specified by the length field, including
CHECKSUM and reserved bytes, must add up to
zero.


















