MultiProcessor Specification
5-2 Version 1.4
Table 5-1. Default Configurations
Default
Config Code
Number
of CPUs
Bus
Type
APIC
Type Variant Schematic
1 2 ISA 82489DX As in Figure 5-1, but without
EISA logic.
2 2 EISA 82489DX Neither timer
IRQ0 nor DMA
chaining
As in Figure 5-1, but without
IRQ0 and IRQ13 connection to
the I/O APIC.
3 2 EISA 82489DX As in Figure 5-1.
4 2 MCA 82489DX As in Figure 5-1, but without
EISA bus logic, with inverters
before I/O APIC inputs 1-15.
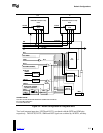
5 2 ISA + PCI Integrated As in Figure 5-2, but without
EISA logic.
6 2 EISA + PCI Integrated As in Figure 5-2.
7 2 MCA + PCI Integrated As in Figure 5-2, but without
EISA bus logic, with inverters
before I/O APIC inputs 1-15.
8-255 Reserved for MP future use.
The default system configurations are designed to support dual-processor systems with fixed
configurations. Systems with dynamically configurable components, for example, a uniprocessor
system with an upgrade socket for the second processor, must always generate the MP
configuration table. Failure to do so may cause the operating system to install the wrong modules
due to erroneous configuration information.
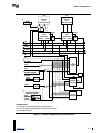
5.1 Discrete APIC Configurations
Figure 5-1 shows the default configuration for systems that use the discrete 82489 APIC. The
Intel486 processor is shown as an example; however, this configuration can also employ Pentium
processors. In Pentium processor systems, PRST is connected to INIT instead of to RESET.