Appendix E: Glossary
STP
E-26
Psion Teklogix 9160 G2 Wireless Gateway User Manual
STP
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is an IEEE 802.1 standard protocol (related to
network management) for MAC bridges that manages path redundancy and
prevents undesirable loops in the network created by multiple active paths between
client stations. Loops occur when there are multiple routes between access points.
STP creates a tree that spans all of the switches in an extended network, forcing
redundant paths into a standby or blocked state. STP allows only one active path at a
time between any two network devices (this prevents the loops) but establishes the
redundant links as a backup if the initial link should fail. If STP costs change, or if
one network segment in the STP becomes unreachable, the spanning tree algorithm
reconfigures the spanning tree topology and re-establishes the link by activating the
standby path. Without STP in place, it is possible that both connections may be
simultaneously live, which could result in an endless loop of traffic on the LAN
Subnet Mask
A Subnet Mask is a number that defines which part of an IP address is the network
address and which part is a host address on the network. It is shown in dotted-
decimal notation (for example, a 24-bit mask is shown as
255.255.255.0
) or as a
number appended to the IP address (for example,
192.168.2.0/24
).
The subnet mask allows a router to quickly determine if an IP address is local or
needs to be forwarded by performing a bitwise AND operation on the mask and the
IP address. For example, if an IP address is
192.168.2.128
and the netmask is
255.255.255.0
, the resulting Network address is
192.168.2.0
.
The bitwise AND operator compares two bits and assigns 1 to the result only if both
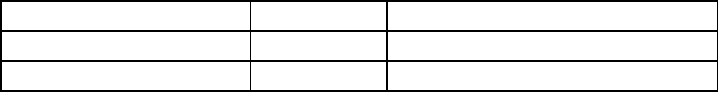
bits are 1. The following table shows the details of the netmask:
Supported Rate Set
The supported rate set defines the transmission rates that are available on this wireless
network. A station may be able to receive data at any of the rates listed in this set. All
stations must be able to receive data at the rates listed in the Basic Rate Set.
IP address
192.168.2.128 11000000 10101000 00000010 10000000
Netmask
255.255.255.0 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000
Resulting network address
192.168.2.0 11000000 10101000 00000010 00000000


















