206
Chapter 13: Programming Features
3. Variables
• Single letters (uppercase letter from A to Z and θ) can be used as variables.
• Defined once in one program, a variable is set as a global variable across all other
stored programs unless redefined.
Hence results calculated in one program can be used by another.
• Only value (numbers) can be set as variables.
• Strings cannot be set as variables.
Setting a variable
Use R to input a specific value or the value of formula into
the variable. Do not use = (comparison operands) to set the
values into variable.
5 → X The variable X is set to the value 5.
MX + B → Y The variable Y is set to the value of formula MX + B.
4. Operands
• Almost all the calculation operands can be used in a program.
• Input an operand directly from the keys (+, –, ×, ÷, sin, cos, log and others) or using
MATH, STAT, LIST, MATRIX and other menus.
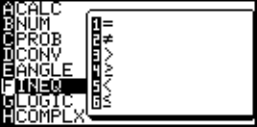
Comparison operands
• The calculator has 6 compari-
son operands.
• Press M F and select
an appropriate comparison
operand.
= Equal ≠ Not equal
> Greater than ≥ Greater than or equal
< Less than ≤ Less than or equal


















