58
Chapter 4: Basic Graphing Features — Basic Keyboard
• When @ " are pressed on the graph screen, the graph
and table are displayed on the same screen.
• When @ " are pressed on the equation input screen,
the graph and equation are displayed on the same screen.
4. Now the right boundary of the graph can be set. Enter the
required value here (“3”, for example), and press E.
Note: The “Xmax=” value cannot be set equal to or smaller than the
value of “Xmin”. If so done, the calculator will display an error
message upon attempting to redraw the graph, and the graph will
not be displayed.
5. The next item “Xscl=” sets the frequency of the X-axis indices.
The default value is “1”. If, for example, the value is set to
“0.5”, then indices will be displayed on the X-axis at incre-
ments of 0.5. Enter the required “Xscl=” value (“0.5”, for
example), and press E.
6. The “Ymin=”, “Ymax=”, and “Yscl=” can be set, as was
described for “Xmin=”, “Xmax=”, and “Xscl=” above.
7. When done, press the G key to draw the graph with the
newly configured window setup.
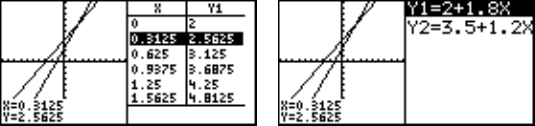
3. Other Useful Graphing Features
": Splits the display vertically, to show the graph on the left side of
the screen while showing the X-Y values in a table on the right.
The cursor is positioned on the table, and can be scrolled up/
down using the { or } keys.
Graph and table Graph and equation


















