C.1.1 UPA
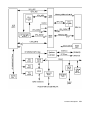
The UltraSPARC port architecture (UPA) provides a packet-based interconnect
between the UPA clients: CPU modules, U2P ASIC, and UPA graphics cards.
Electrical interconnection is provided through four address buses and four data buses.
The four address buses are:
UPA address bus 0 (UPA_AD0)
UPA address bus 1 (UPA_AD1)
UPA address bus 2 (UPA_AD2)
UPA address bus 3 (UPA_AD3)
The four data buses are:
UPA data bus 0 (UPA_DATA0)
UPA data bus 1 (UPA_DATA1)
UPA data bus 2 (UPA_DATA2)
UPA data bus 3 (UPA_DATA3)
UPA_AD0 and UPA_AD1 connect the QSC ASIC to the CPU modules and the U2P
ASIC. UPA_AD2 connects the QSC ASIC to the U2P ASIC. UPA_AD3 connects the
QSC ASIC to the UPA graphics.
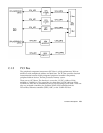
Two processor data buses (UPA_DATA0 and UPA_DATA1) are bidirectional 144-bit
data buses (128 bits of data and 16 bits of ECC) that connect each CPU module to the
XB9+ ASIC. The I/O data bus is a bidirectional 72-bit data bus (64 bits of data and 8
bits of ECC) that connects the U2P ASIC and the UPA graphics (UPA_DATA2) to the
XB9+ ASIC (UPA_DATA3). The UPA graphics do not have ECC, and therefore only
consists of 64 bits of data.
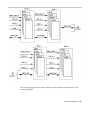
The following table illustrates UPA slot number port addresses.
UPA Slot Number UPA Port ID <4:0>
CPU module slot 0 0x0
CPU module slot 1 01
U2P ASIC 0x1F
The following figure shows the data buses functional block diagram.
252
Sun Enterprise 220R Server Service Manual ♦ January 2000, Revision A