is manufactured. An N_Port is connected directly
to another N_Port in a point-to-point topology. An
N_Port is connected to an F_Port in a fabric topology.
NL_Port In an arbitrated loop topology, information is routed
around a loop. The information is repeated by each
intermediate port until it reaches its destination.
The N_Port that contains this additional loop
functionality is an NL_Port.
Fabric
A switch, or multiple interconnected switches,
that route frames between the originator node
(transmitter) and destination node (receiver).
F_Port The ports within the fabric (fabric port). This port is
called an F_port. Each F_port is assigned a 64-bit
unique node name and a 64-bit unique port name
when it is manufactured. Together, the node name
and port name make up the worldwide name.
FL_Port
An F_Port containing the loop functionality is called
an FL_Port.
Link The physical connection between an N_Port and
another N_Port or an N_Port and an F_Port. A
link consists of two connections, one to transmit
information and one to receive information. The
transmit connection on one node is the receive
connection on the node at the other end of the link.
A link may be optical fibre, coaxial cable, or shielded
twisted pair.
E_Port An expansion port on a switch used to make a
connection between two switches in the fabric.
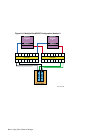
6.2.2 Fibre Channel Topologies
Fibre Channel supports three different interconnect topologies:
• Point-to-point (Section 6.2.2.1)
• Fabric (Section 6.2.2.2)
Using Fibre Channel Storage 6–5