• Arbitrated loop (Section 6.2.2.3)
______________________ Note _______________________
Although it is possible to interconnect an arbitrated loop with
fabric, hybrid configurations are not supported at the present
time, and therefore not discussed in this manual.
6.2.2.1 Point-to-Point
The point-to-point topology is the simplest Fibre Channel topology. In a
point-to-point topology, one N_Port is connected to another N_Port by a
single link.
Because all frames transmitted by one N_Port are received by the other
N_Port, and in the same order in which they were sent, frames require no
routing.
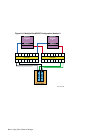
Figure 6–1 shows an example point-to-point topology.
Figure 6–1: Point-to-Point Topology
N_Port
N_Port
Transmit
Receive
Node 1
Node 2
Transmit
Receive
ZK-1534U-AI
6.2.2.2 Fabric
The fabric topology provides more connectivity than point-to-point topology.
The fabric topology can connect up to 2
24
ports.
The fabric examines the destination address in the frame header and routes
the frame to the destination node.
A fabric may consist of a single switch, or there may be several
interconnected switches (up to three interconnected switches is supported).
Each switch contains two or more fabric ports (F_Port) that are internally
6–6 Using Fibre Channel Storage