94 © 2001- 2006 D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
D-Link Unified Access System User Manual
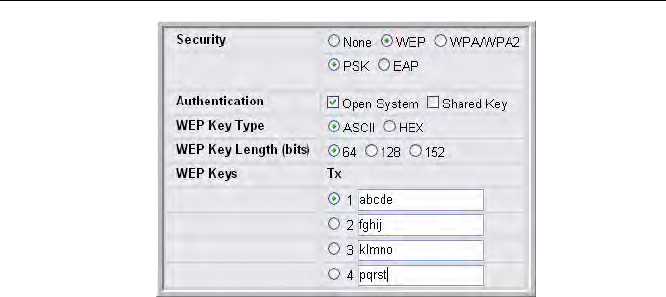
Using Static or Dynamic WEP
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a data encryption protocol for 802.11 wireless networks.
If you select this security mechanism, all wireless clients and access points on the network are
configured with a 64-bit (40-bit secret key + 24-bit initialization vector (IV)), 128-bit (104-bit
secret key + 24-bit IV), or 152-bit (128-bit secret key + 24-bit IV) Shared Key for data
encryption.
Static WEP is not the most secure mode available, but it offers more protection than setting the
security mode to None as it does prevent an outsider from easily sniffing out unencrypted
wireless traffic.
Dynamic WEP is more secure than Static WEP, but you need a RADIUS server to manage the
dynamically generated keys.
WEP encrypts data moving across the wireless network based on a static key. (The encryption
algorithm is a “stream” cipher called RC4.)
If you select WEP as the Security Mode, additional fields display, as Figure 43 shows.
Figure 43. Static WEP Configuration


















