6-91
Configuring the Switch
Load Balancing: Switch Meshing
Configuring the Switch
Caution Because the switch automatically gives faster links a higher priority, the
default STP parameter settings are usually adequate for spanning tree
operation. Because incorrect STP settings can adversely affect network
performance, you should avoid making changes without having a strong
understanding of how STP operates. For more on STP, refer to “Spanning Tree
Protocol (STP)” (page 6-39), and examine the IEEE 802.1d standard.
Filtering/Security in Meshed Switches
Because paths through the mesh can vary with network conditions, configur-
ing filters on meshed ports can create traffic problems that are difficult to
predict, and is not recommended. However, configuring filters on nonmeshed
ports in an edge switch provides you with control and predictability.
IP Multicast (IGMP) in Meshed Switches
Like trunked ports, the switch mesh domain appears as a single port to IGMP.
However, unlike trunked ports, IGMP protocol and multicast traffic may be
sent out over several links in the mesh in the same manner as broadcast
packets.
802.1Q VLANs in Meshed Switches
In a network having a switch mesh domain and multiple VLANs configured,
all VLANs must be configured on each meshed switch, even if no ports on the
switch are assigned to any VLAN. (The switch mesh is a member of all VLANs
configured on the network.)
When VLANs are configured and activated, the mesh is seen as a single entity
by each VLAN. All ports in the mesh domain are members of all VLANs and
can be used to forward traffic for any VLAN. However, the non-mesh ports on
edge switches that allow traffic to move between the mesh and non-meshed
devices belong to specific VLANs and do not allow packets originating in a
specific VLAN to enter non-meshed devices that do not belong to that same
VLAN. (It is necessary to use a router to communicate between VLANs.) For
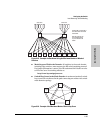
example, in the following illustration, traffic from host A entering the mesh
can only exit the mesh at the port for hosts B and E. Traffic from host A for
any other host (such as C or D) will be dropped because only hosts B and E
are in the same VLAN as host A.