6-101
Configuring the Switch
IP Multicast (IGMP) Features—Multimedia Traffic Control
Configuring the Switch
Role of the Switch
When IGMP is enabled on the switch, it examines the IGMP packets it receives:
■ To learn which of its ports are linked to IGMP hosts and multicast routers/
queriers belonging to any multicast group
■ To become a querier if a multicast router/querier is not discovered on the
network
Once the switch learns the port location of the hosts belonging to any partic-
ular multicast group, it can direct group traffic to only those ports, resulting
in bandwidth savings on ports where group members do not reside. The
following example illustrates this operation.
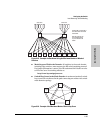
Figure 6-67 on page 6-102 shows a network running IGMP.
■ PCs 1 and 4, switch 2, and all of the routers are members of an IP multicast
group. (The routers operate as queriers.)
■ Switch 1 ignores IGMP traffic and does not distinguish between IP multi-
cast group members and non-members. Thus, it is sending large amounts
of unwanted multicast traffic out the ports to PCs 2 and 3.
■ Switch 2 is recognizing IGMP traffic and learns that PC 4 is in the IP
multicast group receiving multicast data from the video server (PC X).
Switch 2 then sends the multicast data only to the port for PC 4, thus
avoiding unwanted multicast traffic on the ports for PCs 5 and 6.