6-133
Configuring the Switch
Class of Service (CoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively
Configuring the Switch
If a packet is not in an 802.1Q tagged VLAN environment, the above settings
control only to which outbound queue the packet goes, and no 802.1p priority
is added to the packet. However, if the packet is in an 802.1Q tagged VLAN
environment, then the above setting is also added to the packet as an 802.1p
priority that can be used by downstream devices and applications, as indicated
in the next table.
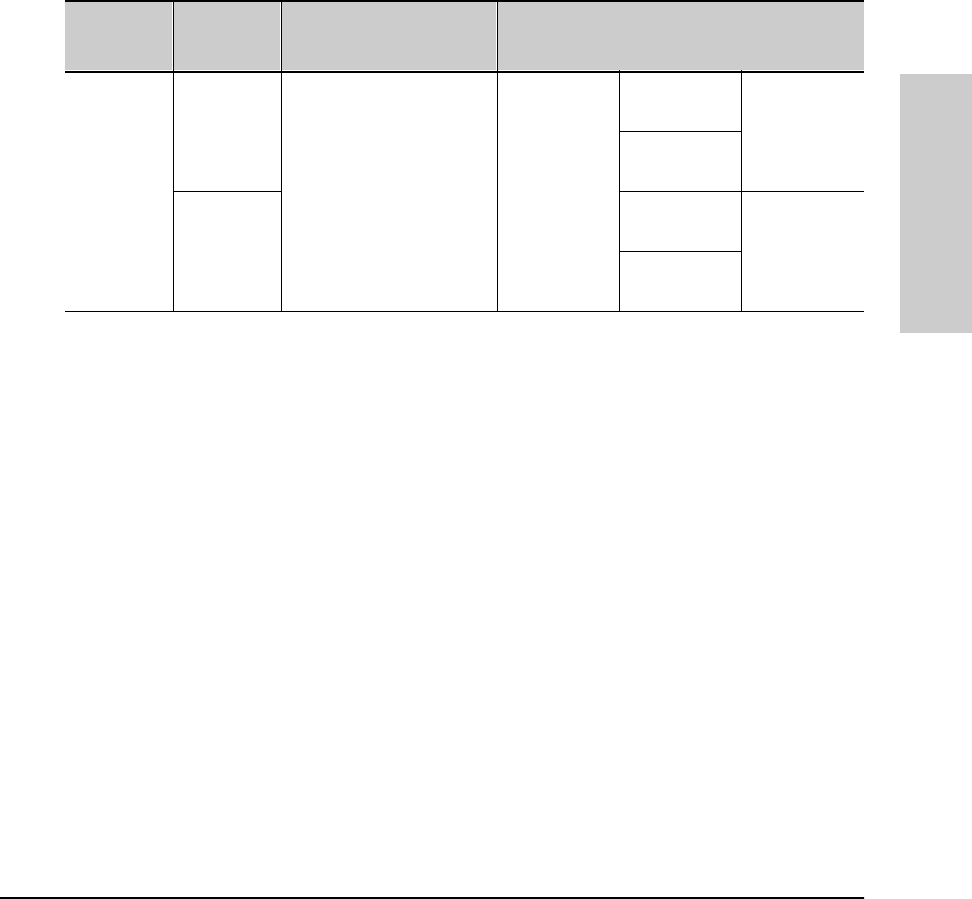
Table 6-6. Mapping Priority Settings to Device Queues
Criteria for Prioritizing Outbound Packets
You can configure CoS prioritization on the basis of five packet criteria,
evaluated in the following order:
1. Device Priority (destination or source IP address)
2. IP Type of Service (ToS) field
3. Protocol Priority (IP, IPX, ARP, DEC LAT, AppleTalk, SNA, and NetBeui)
4. VLAN Priority
5. Incoming 802.1p Priority (present in tagged VLAN environments)
If more than one criteria is present in a packet, the switch applies a precedence
scheme to the criteria and then uses only the CoS configuration for the packet
criteria that has the highest precedence. For example, if CoS assigns high
priority to “red” VLAN packets, but normal priority to IP packets, since
Protocol Priority has precedence over VLAN priority, IP packets on the “red”
VLAN will be set to normal priority. See Table 6-7. Priority Criteria and
Precedence on page 6-134 for more information.
Priority
Setting in
the Switch
Outbound
Port Queues
in the Switch
802.1p Priority Setting
Added to Tagged VLAN
Packet Leaving the Switch
Queue Assignment in Downstream Devices With:
8 Queues 4 Queues 2 Queues
1 Normal 1 (low priority) Queue 1 Queue 1
2 Normal 2 Queue 2 Queue 1
0 Normal 0 (normal priority) Queue 3 Queue 2
3 Normal 3 Queue 4
4 High 4 Queue 5 Queue 3
5 High 5 Queue 6 Queue 2
6 High 6 Queue 7 Queue 4
7 High 7 (high priority) Queue 8


















