6-100
Configuring the Switch
IP Multicast (IGMP) Features—Multimedia Traffic Control
Configuring the Switch
How IGMP Operates
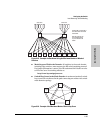
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an internal protocol of
the Internet Protocol (IP) suite. IP manages multicast traffic by using
switches, multicast routers, and hosts that support IGMP. (In Hewlett-Pack-
ard’s implementation of IGMP, a multicast router is not necessary as long as
a switch is configured to support IGMP with the querier feature enabled.) A
set of hosts, routers, and/or switches that send or receive multicast data
streams to or from the same source(s) is termed a multicast group, and all
devices in the group use the same multicast group address. The multicast
group running version 2 of IGMP uses three fundamental types of messages
to communicate:
■ Query: A message sent from the querier (multicast router or switch)
asking for a response from each host belonging to the multicast group. If
a multicast router supporting IGMP is not present, then the switch must
assume this function in order to elicit group membership information
from the hosts on the network. (If you need to disable the querier feature,
you can do so through the console, using the IGMP configuration MIB.
Refer to “Changing the Querier Configuration Setting” on page 6-105.)
■ Report: A message sent by a host to the querier to indicate that the host
wants to be or is a member of a given group indicated in the report
message.
■ Leave Group: A message sent by a host to the querier to indicate that the
host has ceased to be a member of a specific multicast group.
Thus, IGMP identifies members of a multicast group (within a subnet) and
allows IGMP-configured hosts (and routers) to join or leave multicast groups.
IGMP Data. To display data showing active group addresses, reports, que-
ries, querier access port, and active group address data (port, type, and
access), see “IP Multicast (IGMP) Status” on page 7-19.