APPLICATION
2.3 Timers
2-31
4513/4514 Group User’s Manual
(4) CNTR1 output control: square wave output control
Outline: The output/stop of square wave from timer 3 every timer 4 underflow can be controlled.
Specifications: 4 kHz square wave is output from timer 3 at system clock frequency f(X
IN) = 4.0
MHz. Also, timer 4 controls ON/OFF of square wave every constant period.
Figure 2.3.6 shows the setting example of CNTR1 output.
(5) Timer operation: timer start by external input
Outline: The constant period can be measured by external input.
Specifications: Timer 1 operates by INT0 input as a trigger and an interrupt occurs after 1 ms.
Figure 2.3.7 and Figure 2.3.8 show the setting example of timer start.
(6) Watchdog timer
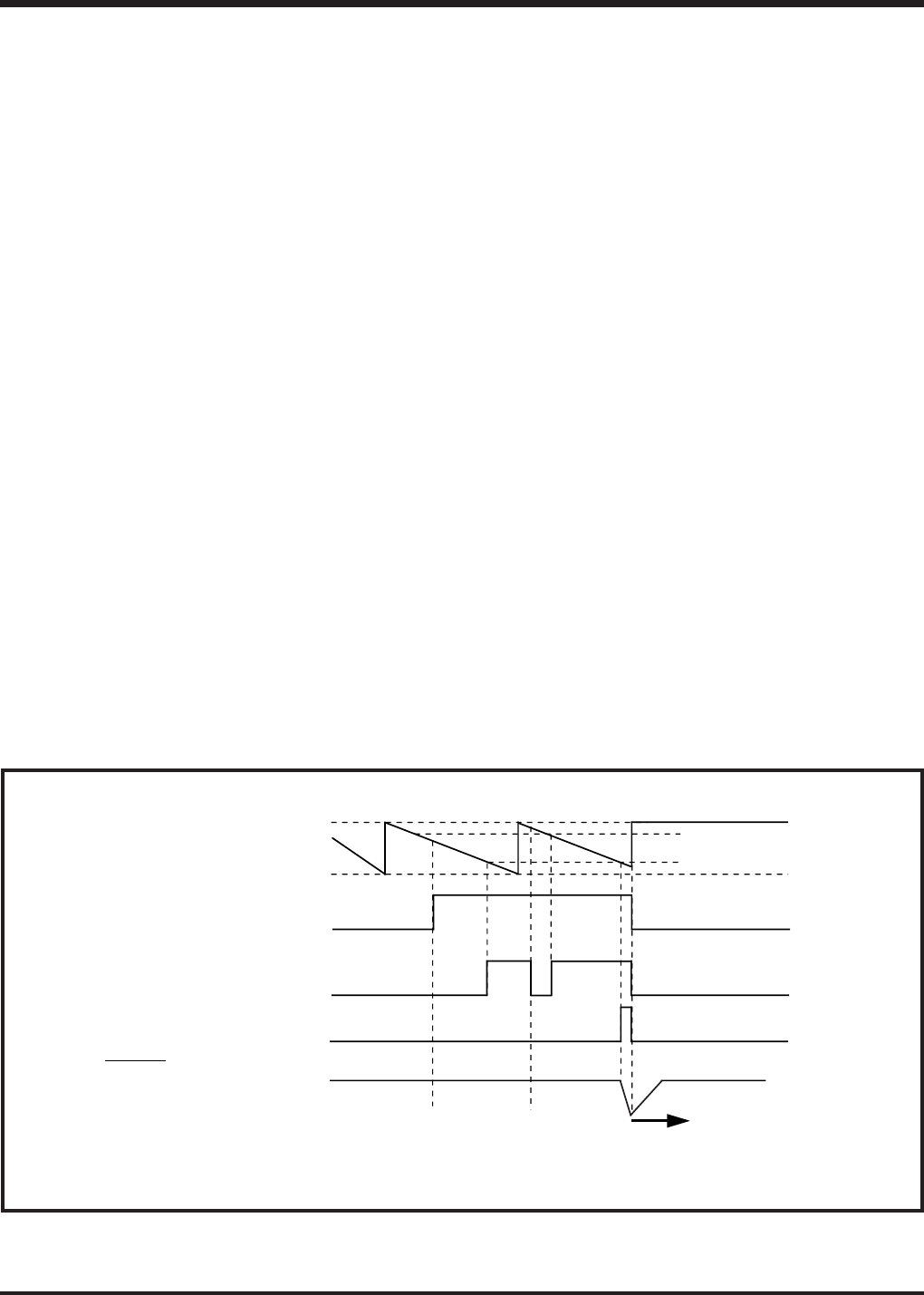
Watchdog timer provides a method to reset the system when a program run-away occurs.
In the 4513/4514 Group, bit 15 of 16-bit timer is counted twice for the watchdog timer.
Accordingly, when the watchdog timer function is set to be valid, execute the WRST instruction at
a certain period which consists of timer 16-bit timers’ 32767 counts or less (execute WRST instruction
at a cycle of 32766 machine cycles or less).
Outline: Execute the WRST instruction in 16-bit timer’s 32767 counts at the normal operation. If a
program runs incorrectly, the WRST instruction is not executed and system reset occurs.
Specifications: System clock frequency f(X
IN) = 4.0 MHz is used, and program run-away is detected
by executing the WRST instruction in 24 ms.
Figure 2.3.2 shows the watchdog timer function, and Figure 2.3.9 shows the example of watchdog
timer.
Fig. 2.3.2 Watchdog timer function
FFFF16
0000 16
3FFF16
BFFF16
System reset
WRST
instruction
execution
WRST
instruction
execution
Value of timer WDT
WEF flag
WDF1 flag
WDF2 flag
RESET pin output