3-14
APPENDIX
3.2 Typical characteristics
4513/4514 Group User’s Manual
3.2.5 A-D converter typical characteristics
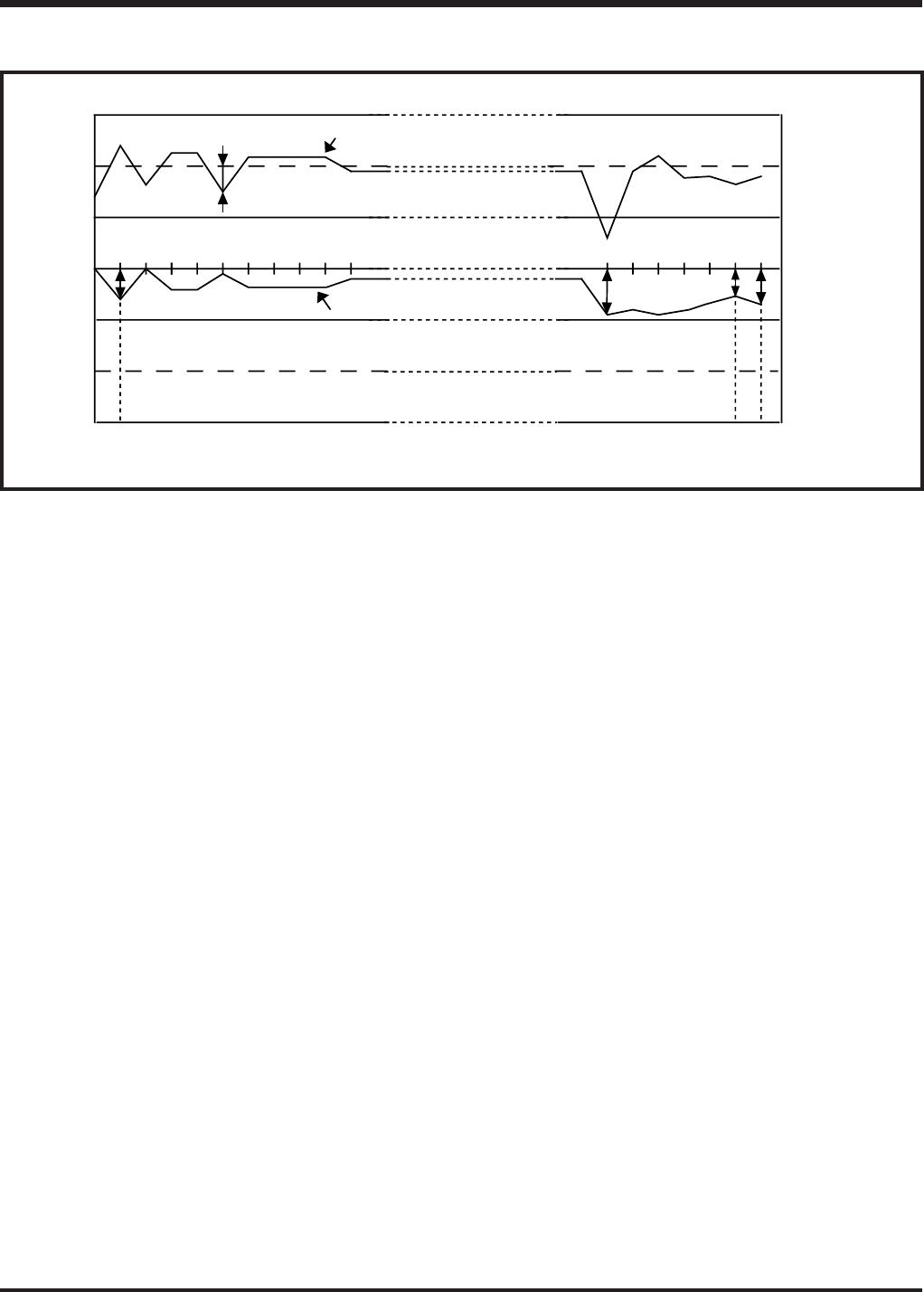
Fig. 3.2.1 A-D conversion characteristics data
Figure 3.2.1 shows the A-D accuracy measurement data.
(1) Non-linearity error......................... This means a deviation from the ideal characteristics between V0 to
V1022 of actual A-D conversion characteristics. In Figure 3.2.1, it is
(➃–➀)/1LSB.
(2) Differencial non-linearity error .... This means a deviation from the ideal characteristics between the
input voltages V0 to V1022 necessary to change the output data to
“1.” In Figure 3.2.1, this is ➁/1LSB.
(3) Zero transition error ..................... This means a deviation from the ideal characteristics between the
input voltages 0 to VDD when the output data changes from “0” to “1.”
In Figure 3.2.1, this is the value of ➀.
(4) Full-scale transition error............. This means a deviation from the ideal characteristics between the
input voltages 0 to VDD when the output data changes from “1022”
to “1023.” In Figure 3.2.1, this is the value of ➄.
(5) Absolute accuracy ........................ This menas a deviation from the ideal characteristics between 0 to
VDD of actual A-D conversion characteristics. In Figure 3.2.1, this is
the value of ERROR in each of ➀, ➂, ➃ and ➄.
For the A-D converter characteristics, refer to the section 3.1 Electrical characteristics.
+1LSB
0
-1LSB
1LSB WIDTH
1LSB WIDTH [
mV]
1022 1023
ERROR
0
1
ERROR [mV]
➃
➁
0
➀
➂
30
-30
➄
