1-40
HARDWARE
4513/4514 Group User’s Manual
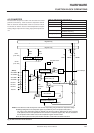
FUNCTION BLOCK OPERATIONS
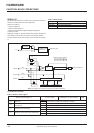
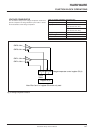
Table 13 Processing sequence of data transfer from master to slave
1-byte data is serially transferred on this process. Subsequently, data
can be transferred continuously by repeating the process from *.
When an external clock is selected as a synchronous clock, the
clock is not controlled internally. Control the clock externally be-
cause serial transfer is performed as long as clock is externally
input. (Unlike an internal clock, an external clock is not stopped
when serial transfer is completed.) However, the SIOF flag is set to
“1” when the clock is counted 8 times after executing the SST in-
struction. Be sure to set the initial level of the external clock to “H.”
Master (transmission)
[Initial setting]
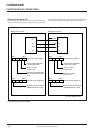
• Setting the serial I/O mode register J1 and inter-
rupt control register V2 shown in Figure 24.
TJ1A and TV2A instructions
• Setting the port received the reception enable
signal (SRDY) to the input mode.
(Port D5 is used in this example)
SD instruction
* [Transmission enable state]
• Storing transmission data to serial I/O register SI.
TSIAB instruction
[Transmission]
•Check port D5 is “L” level.
SZD instruction
•Serial transfer starts.
SST instruction
•Check transmission completes.
SNZSI instruction
•Wait (timing when continuously transferring)
Slave (reception)
[Initial setting]
• Setting serial I/O mode register J1, and interrupt control register V2 shown in
Figure 24.
TJ1A and TV2A instructions
• Setting the port transmitted the reception enable signal (SRDY) and outputting
“H” level (reception impossible).
(Port D5 is used in this example)
SD instruction
*[Reception enable state]
• The SIOF flag is cleared to “0.”
SST instruction
• “L” level (reception possible) is output from port D5.
RD instruction
[Reception]
• Check reception completes.
SNZSI instruction
• “H” level is output from port D5.
SD instruction
[Data processing]