17-80 Riverstone Networks RS Switch Router User Guide Release 8.0
Configuring L2 Tunnels MPLS Configuration
L2 Tunneling Based on Ports Configuration Examples
The FEC-to-label binding for a virtual circuit can be based on the port on which traffic arrives. One or more incoming
ports are mapped to a logical customer ID number, which is then mapped to an FEC.
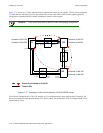
In Figure 17-18, ports gi.6.1 on R1 and gi.12.1 on R3 are mapped to customer ID 1. Ports gi.3.1 on R1 and gi.13.1 on
R3 are mapped to customer ID 2. The customer IDs are mapped to VC labels that are distributed via LDP. You can
choose to have either untagged or 802.1q tagged frames transported across the tunnel LSP; the configuration for
transporting untagged packets is shown. The tunnel LSP can use either LDP or RSVP as the signaling protocol;
configuration commands for both LDP and RSVP tunnel signaling are shown.
Timesaver
Click on the router name (in blue) to see the corresponding configuration.
Figure 17-18 Tunneling of multiple virtual circuits based on ports (untagged
frames)
The following is the configuration for R1:
! Configure router loopback
interface add ip lo0 address-netmask 111.1.1.1/32
! Make gi.4.1 a trunk port that does not send out 802.1q tagged frames
vlan make trunk-port gi.4.1 untagged
! Configure the LDP peers and label bindings
ldp add interface lo0
ldp add remote-peer 111.1.1.3
adds R3 as LDP peer
ldp map ports gi.6.1 customer-id 1
maps port gi.6.1 to customer-id 1
ldp map ports gi.3.1 customer-id 2
maps port gi.3.1 to customer-id 2
ldp add l2-fec customer-id 1 to-peer 111.1.1.3
sends label mapping for customer-id 1 to R3
ldp add l2-fec customer-id 2 to-peer 111.1.1.3
sends label mapping for customer-id 2 to R3
ldp start
L2 Tunnel (RSVP or LDP)
gi.6.1
gi.12.1
Virtual Circuit based on Port for Customer ID 1 (LDP)
R3
R1
111.1.1.1/16 111.1.1.3/16
gi.3.1
gi.13.1
111.1.1.2/16
R2
Virtual Circuit based on Port for Customer ID 2 (LDP)
gi.4.1 gi.14.1 gi.15.1
gi.3.2