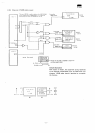
M
7
3500
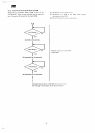
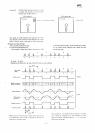
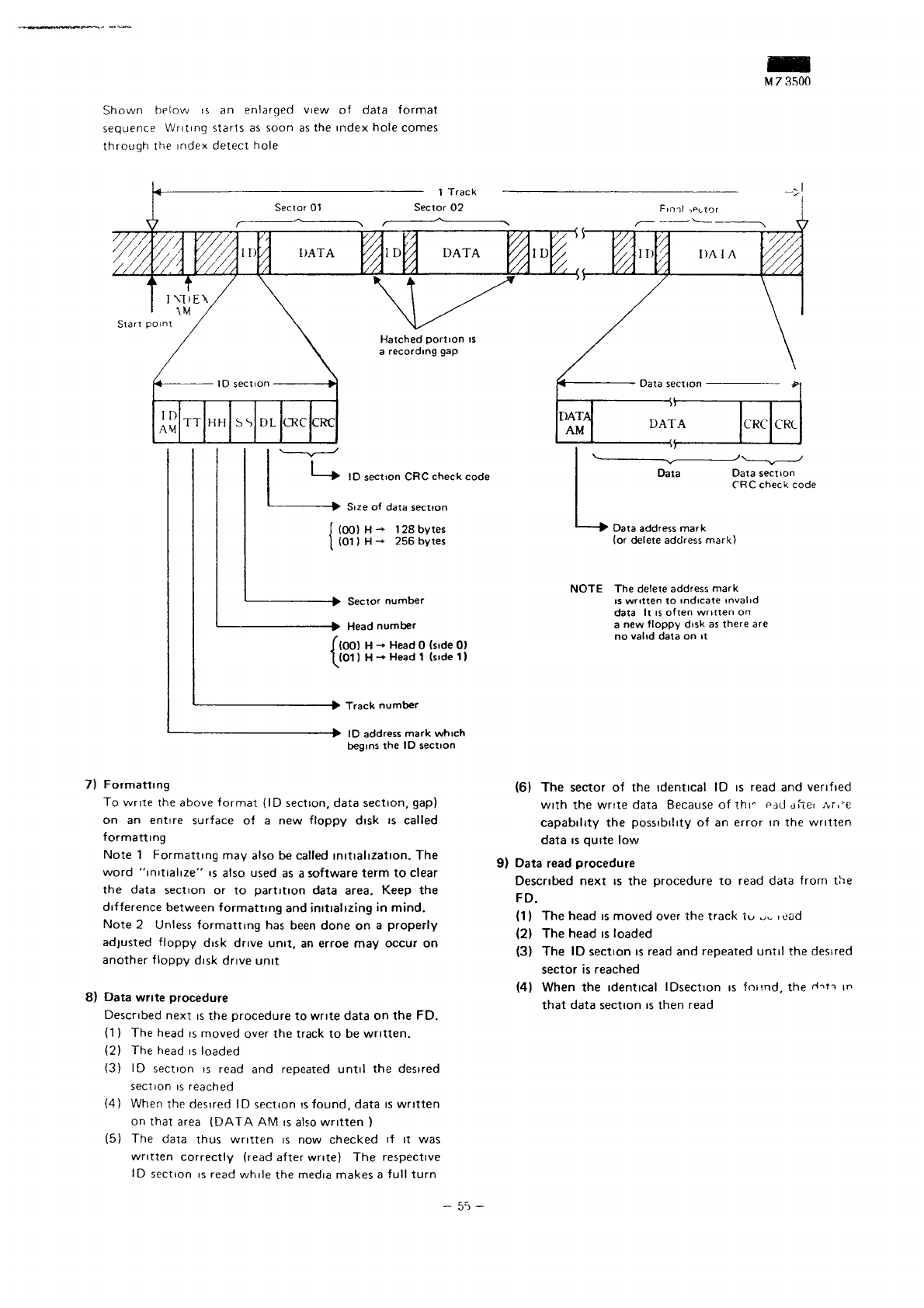
Shown
below
is an
enlarged
view
of
data format
sequence
Writing
starts
as
soon
as the
index hole comes
through
the
index
detect hole
1
Track
Sector
01
Sector
02
Firnl
^p
DATA
DATA
IU
II)
DA I A
<
[
t
INDEX
\M
Start
point
Hatched
portion
is
a
recording
gap
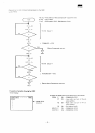
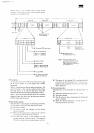
ID
AM
TT
HH
SS
DL
CRC
CRC
DATA
AM
51
DATA
CRC
CRC
ID
section
CRC
check
code
Size
of
data
section
(00)
H — 128
bytes
(01)
H — 256
bytes
Sector
number
Head
number
(00)
H -»
Head
0
(side
0)
(01)
H -*
Head
1
(side
1)
•
Track
number
•
ID
address
mark
which
begins
the ID
section
Data
Data
section
CRC
check
code
'
Data
address
mark
(or
delete
address
mark)
NOTE
The
delete
address
mark
is
written
to
indicate
invalid
data
It is
often
written
on
a
new
floppy
disk
as
there
are
no
valid
data
on it
7)
Formatting
To
write
the
above
format
(ID
section, data section, gap)
on an
entire
surface
of a new
floppy
disk
is
called
formatting
Note
1
Formatting
may
also
be
called
initialization.
The
word
"initialize"
is
also used
as a
software
term
to
clear
the
data section
or to
partition
data area. Keep
the
difference
between
formatting
and
initializing
in
mind.
Note
2
Unless
formatting
has
been
done
on a
properly
adjusted
floppy
disk drive
unit,
an
erroe
may
occur
on
another
floppy
disk drive
unit
8)
Data write procedure
Described
next
is the
procedure
to
write
data
on the FD.
(1)
The
head
is
moved over
the
track
to be
written.
(2)
(3)
(4)
The
head
is
loaded
ID
section
is
read
and
repeated
until
the
desired
section
is
reached
When
the
desired
ID
section
is
found,
data
is
written
on
that
area
(DATA
AM is
also
written
)
(5)
The
data
thus written
is now
checked
if it was
written correctly
(read
after
write)
The
respective
ID
section
is
read while
the
media
makes
a
full
turn
(6)
The
sector
of the
identical
ID is
read
and
verified
with
the
write
data
Because
of thr pad
dftei
Ar.'e
capability
the
possibility
of an
error
in the
written
data
is
quite
low
9)
Data
read
procedure
Described
next
is the
procedure
to
read data
from
the
FD.
(1)
The
head
is
moved over
the
track
tu -^ i ead
(2) The
head
is
loaded
(3) The ID
section
is
read
and
repeated
until
the
desired
sector
is
reached
(4)
When
the
identical
IDsection
is
found,
the
<~i-m
IP
that
data section
is
then
read