A Primer on Electro-Static Discharge Teledyne API T803 CO2/O2 Analyzer Operation Manual
228
As long as my analyzer is properly installed, it is safe from damage caused
by static discharges: It is true that when properly installed the chassis ground of
your analyzer is tied to earth ground and its electronic components are prevented
from building static electric charges themselves. This does not prevent
discharges from static fields built up on other things, like you and your clothing,
from discharging through the instrument and damaging it.
13.4. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF STATIC CONTROL
It is impossible to stop the creation of instantaneous static electric charges. It is
not, however difficult to prevent those charges from building to dangerous levels
or prevent damage due to electro-static discharge from occurring.
13.4.1. GENERAL RULES
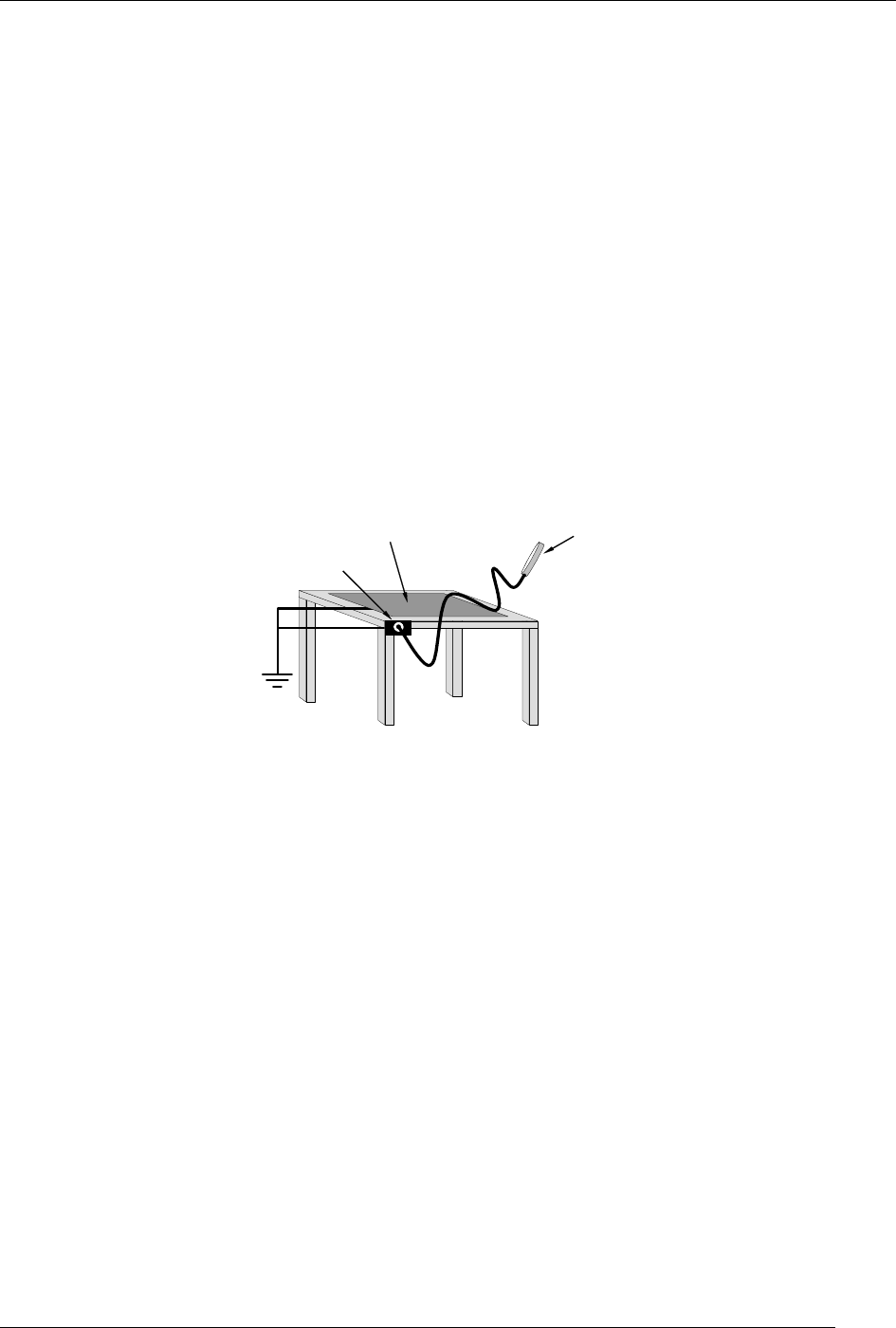
Only handle or work on all electronic assemblies at a properly set up ESD station.
Setting up an ESD safe workstation need not be complicated. A protective mat
properly tied to ground and a wrist strap are all that is needed to create a basic
anti-ESD workstation.
Wrist Str
a
Protective Mat
Ground Point
Figure 13-2: Basic Anti-ESD Workbench
For technicians that work in the field, special lightweight and portable anti-ESD
kits are available from most suppliers of ESD protection gear. These include
everything needed to create a temporary anti-ESD work area anywhere.
Always wear an Anti-ESD wrist strap when working on the electronic
assemblies of your analyzer. An anti-ESD wrist strap keeps the person wearing
it at or near the same potential as other grounded objects in the work area and
allows static charges to dissipate before they can build to dangerous levels. Anti-
ESD wrist straps terminated with alligator clips are available for use in work
areas where there is no available grounded plug.
Also, anti-ESD wrist straps include a current limiting resistor (usually around one
meg-ohm) that protects you should you accidentally short yourself to the
instrument’s power supply.
Simply touching a grounded piece of metal is insufficient. While this may
temporarily bleed off static charges present at the time, once you stop touching
the grounded metal new static charges will immediately begin to re-build. In
some conditions, a charge large enough to damage a component can rebuild in
just a few seconds.
07276B DCN6418


















