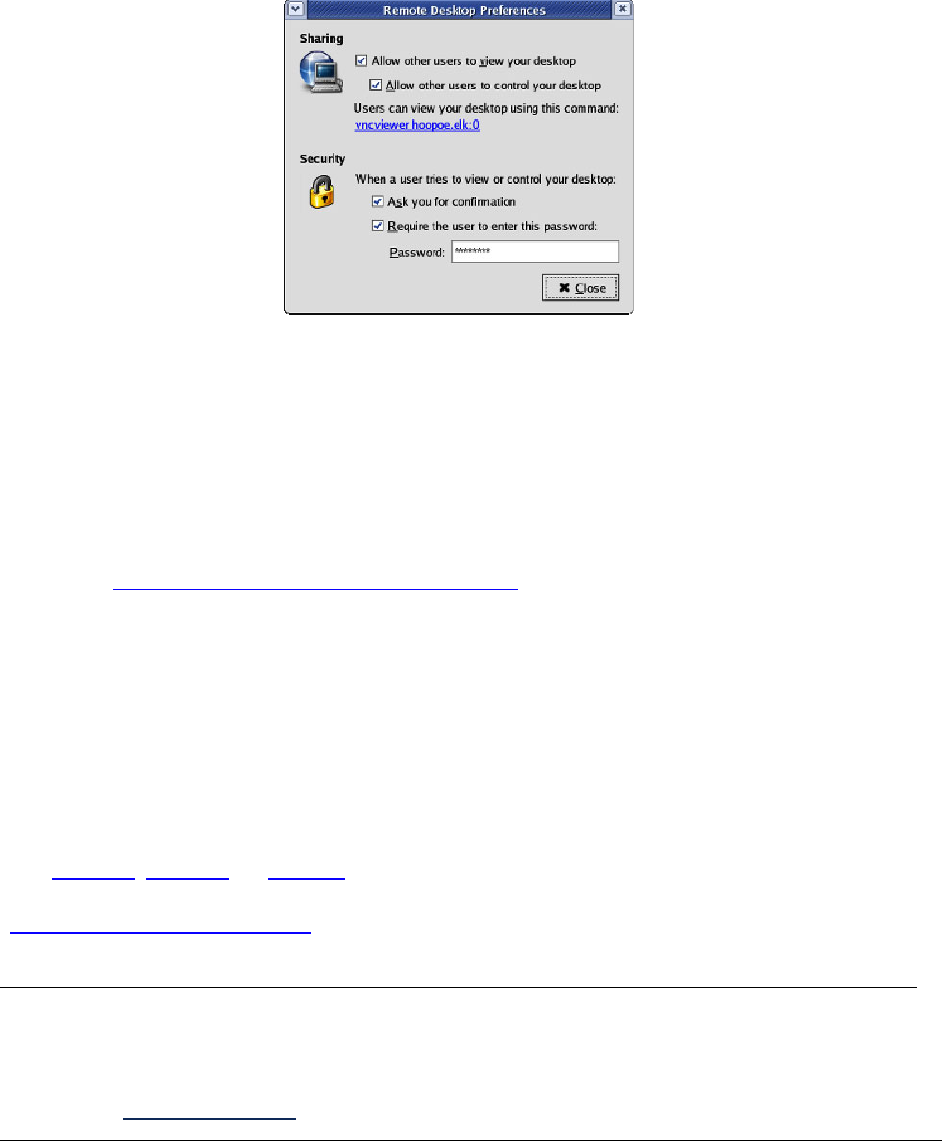
86
To set up a persistent VNC server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4:
o Set a password using vncpasswd
o Edit /etc/sysconfig/vncservers
o Enable the service with chkconfig vncserver on
o Start the service with service vncserver start
o Edit /home/username/.vnc/xstartup if you want a more advanced session than just twm
and an xterm
C. For Macintosh servers (and clients):
OSXvnc http://www.redstonesoftware.com/vnc.html
is a robust, full-featured VNC server for Mac
OS X that allows any VNC client to remotely view and/or control Mac OS X machine. OSXvnc is
supported by Redstone Software
D. Most other operating systems (Solaris, HPUX, PalmOS etc) either come with VNC bundled, or have
third-party VNC software that you can download
6.9.2 Install, configure and connect the VNC Viewer
VNC is truly platform-independent, so a VNC Viewer on any operating system can connect to a VNC
Server on any other operating system. There are Viewers (and Servers) from a wide selection of sources
(e.g. UltraVNC
TightVNC or RealVNC) for most operating systems. There are also a wealth of Java
viewers available so that any desktop can be viewed with any Java-capable browser
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VNC
lists many of the VNC Viewers sources).
Install the VNC Viewer software and set it up for the appropriate speed connection
Note To make VNC faster, when you set up the Viewer:
Set encoding to ZRLE (if you have a fast enough CPU)
Decrease color level (e.g. 64 bit)
Disable the background transmission on the Server or use a plain wallpaper
(Refer to http://doc.uvnc.com
for detailed configuration instructions)
To establish the VNC connection, first configure the VNC Viewer, entering the VNC Server IP
address