5-31
(Y-ICPT) ... y-intercept
(ISCT) ... Intersection of two graphs
(E)(Y-CAL) ... y-coordinate for given x-coordinate
(E)(X-CAL) ... x-coordinate for given y-coordinate
(E)(°dx) ... Integral value for a given range
4. When there are multiple graphs on the screen, the selection cursor (I) is located at the
lowest numbered graph. Press D and A to move the cursor to the graph you want to
select.
5. Press U to select the graph where the cursor is located and display the value produced by
the analysis.
When an analysis produces multiple values, press C to calculate the next value.
Pressing B returns to the previous value.
• Either of the following can cause poor accuracy or even make it impossible to obtain
solutions.
- When the graph of the solution obtained is a point of tangency with the
x-axis
- When a solution is an inflection point
I Calculating the Point of Intersection of Two Graphs
Use the following procedure to calculate the point of intersection of two graphs.
1. Draw the graphs.
2. Press (G-SLV)(ISCT). When there are three or more graphs, the selection cursor
(I) appears at the lowest numbered graph.
3. Press D and A to move the cursor to the graph you want to select.
4. Press U to select the first graph, which changes the shape of the cursor from I to
R
.
5. Press D and A to move the cursor to the second graph.
6. Press U to calculate the point of intersection for the two graphs.
When an analysis produces multiple values, press C to calculate the next value.
Pressing B returns to the previous value.
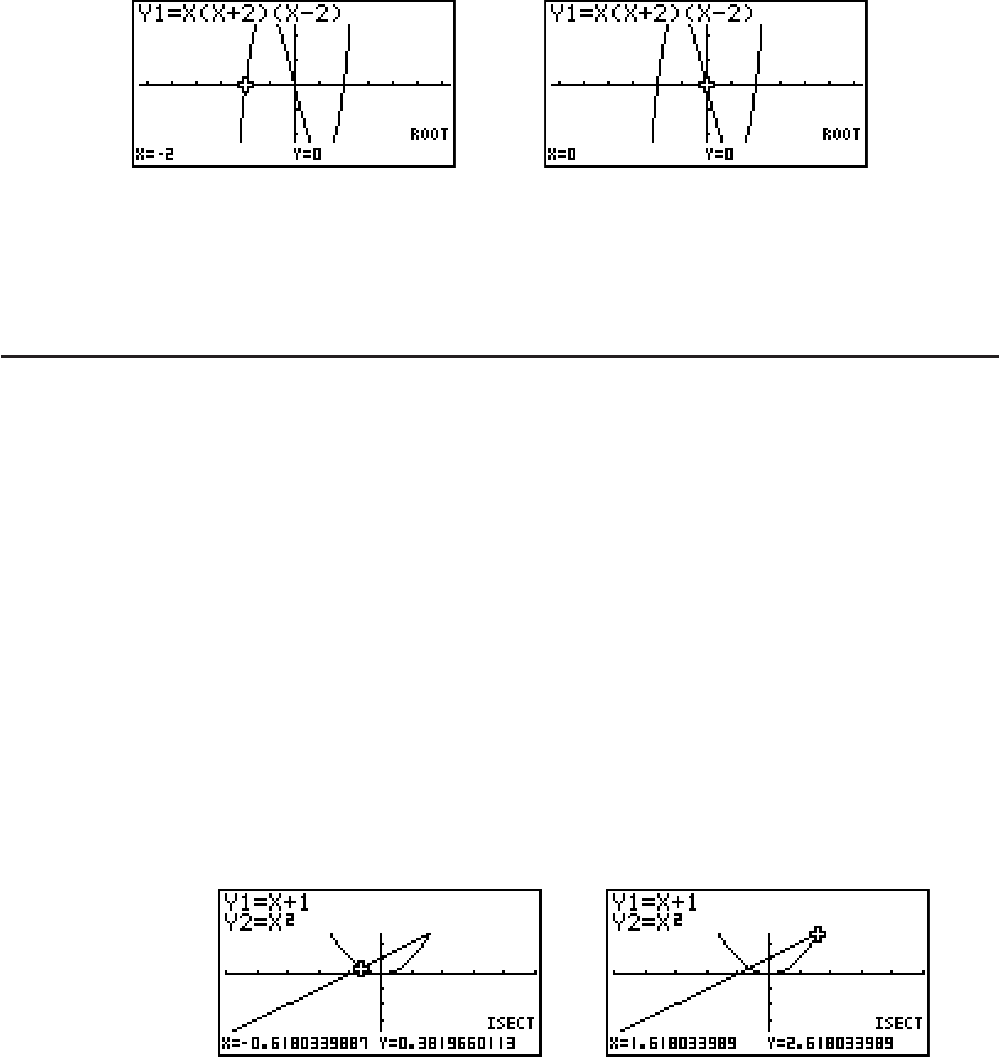
Example Graph the two functions shown below, and determine the point of
intersection between Y1 and Y2.
Y1 =
x + 1, Y2 = x
2
