8-5
4. Each press of U or (SRC) causes the cursor to jump
to the next instance of the data you specified.*
2
*
1
The message “Not Found” appears when the search data you specify cannot be found in the
program.
*
2
If there are no more instances of the data you specified, the search operation ends.
• You cannot specify the newline symbol (=) or display command (<) for the search data.
• Once the contents of the program are on the screen, you can use the cursor keys to move
the cursor to another location before searching for the next instance of the data. Only the
part of the program starting from the current cursor location is searched when you press U.
• Once the search finds an instance of your data, inputting characters or moving the cursor
causes the search operation to be cancelled.
• If you make a mistake while inputting characters to search for, press to clear your input
and re-input from the beginning.
4. File Management
I Searching for a File
S To find a file using initial character search
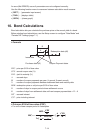
Example To use initial character search to recall the program named OCTA
1. While the program list is on the display, press (E)(SRC) and input the initial
characters of the file you want to find.
(E)(SRC)
H(O)((C)(T)
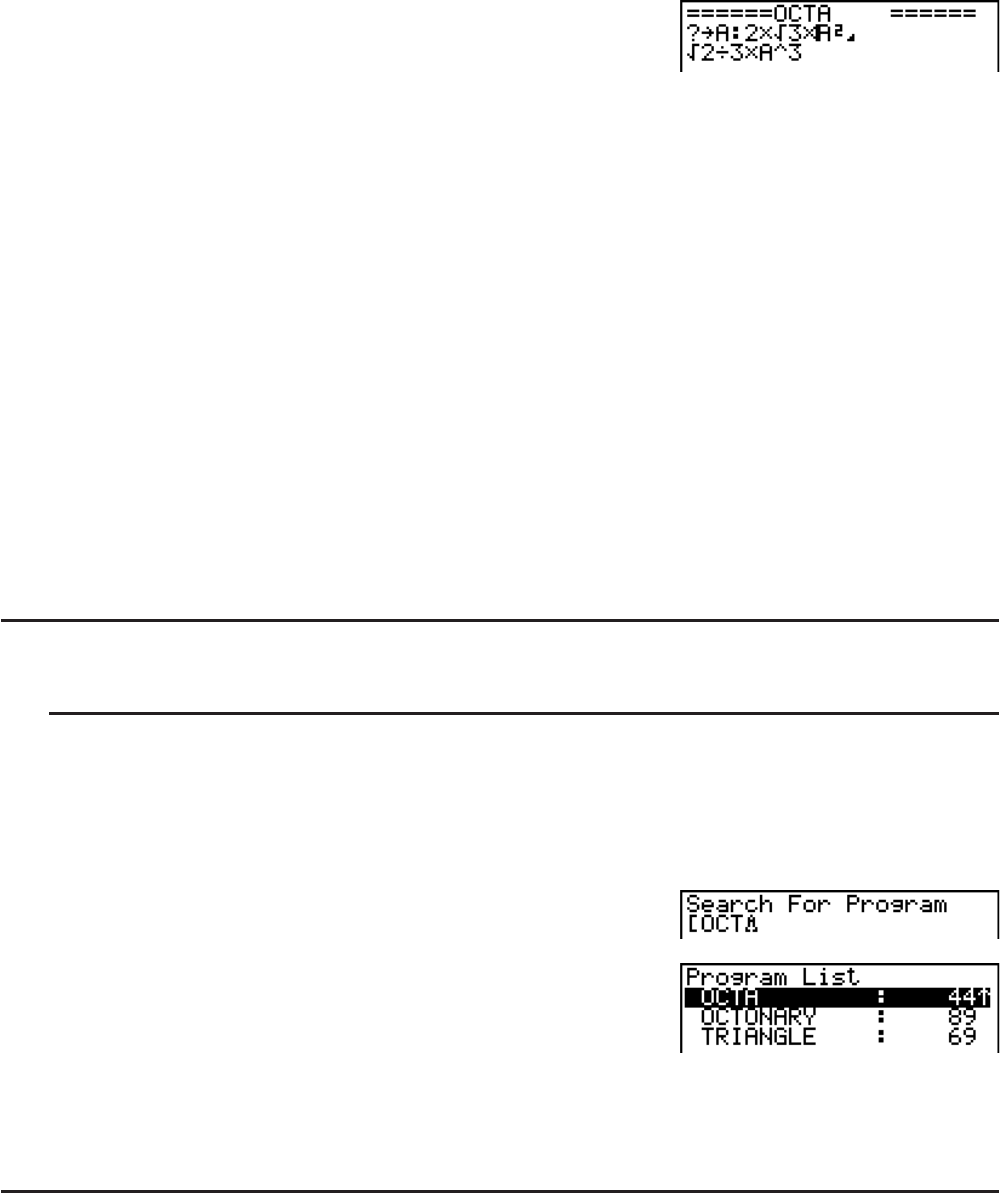
2. Press U to search.
• The name that starts with the characters you input
highlights.
• If there is no program whose file name starts with the characters you input, the message
“Not Found” appears on the display. If this happens, press ) to clear the error message.
I Editing a File Name
1. While the program list is on the display, use D and A to move the highlighting to the file
whose name you want to edit and then press (E)(REN).
2. Make any changes you want.
3. Press U to register the new name and return to the program list.
The program list is resorted according to the changes you made in the file name.
• If the modifications you make result in a file name that is identical to the name of a program
already stored in memory, the message “Already Exists” appears. When this happens, you
can perform either of the following two operations to correct the situation.