CHAPTER 4 Adaptive Server IQ Indexes
153
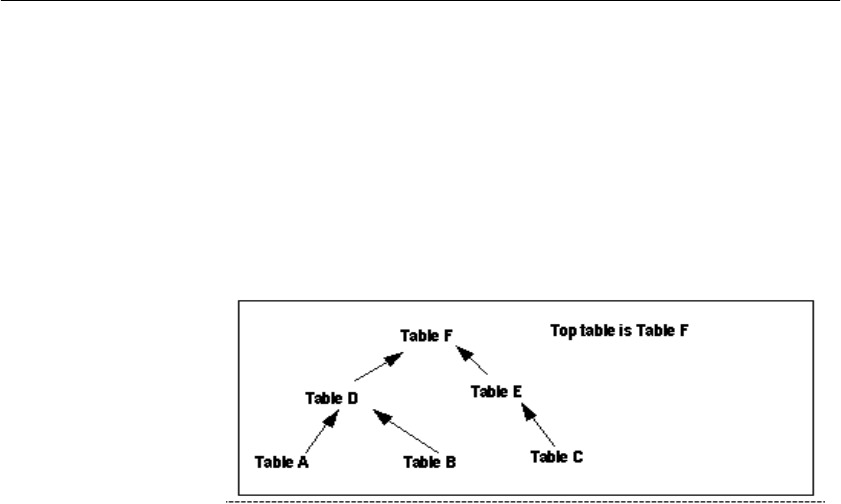
Adaptive Server IQ join hierarchies have one table at the top of the tree where
the join ends. This table, known as the top table, does not connect to any other
tables, although other tables connect to it. The top table always represents the
“many” side in a one-to-many relationship.
Depending on the complexity of the join, there could be a straight line of tables
down to the bottom of the tree and the beginning of the join, or there could be
many branches off to the side as you move down the tree. The following figure
shows a join hierarchy with two branches.
Figure 4-1: Hierarchy of a join relationship
In a join hierarchy:
• A table can occur only once
• A table can only connect out once (one arrow leaving it)
• All tables must be connected
Columns in the join index
Suppose that you joined Tables A through E in a join index called ABCDE. If
each table has two columns of data, expect the join index to have a total of
fourteen columns. Adaptive Server IQ creates an additional column, the
ROWID column, for each of the joined tables except the top table. In this case,
there are ten columns (two from each of the five tables), plus four
ROWID
columns.
You can use the
NOTIFY option of the LOAD TABLE or INSERT statement to
receive notification messages when you insert into a column index. In these
messages, the name of each column in a join index, including the
ROWID
column, is identified.


















