Fiber Matrix 6400 Switcher • Maintenance and Modications
7-2
Maintenance and Modifications
Removing and Installing the I/O Board or Blank Panel
W
The Fiber Matrix 6400 fiber optic I/O boards output continuous invisible
light, which may be harmful and dangerous to the eyes; use with caution.
•
Do not look into the rear panel fiber optic cable connectors or into the
fiber optic cables themselves.
•
Plug the attached dust caps into the optical transceivers when the fiber
optic cable is unplugged.
N
As factory configured, the fiber optic I/O boards are configured as either
100 percent singlemode or 100 percent multimode, but you can remove a fiber
optic transceiver module (one input and one output) of one transmission mode
and replace it with a block of the other transmission mode.
You can mix transmission mode transceiver modules on a fiber optic I/O board,
provided that you ensure that each fiber cable and connected devices are the
appropriate transmission mode for the transceiver module.
Typically, singlemode fiber has a yellow jacket and multimode cable has an
orange jacket.
N
Unlike the FOX 500 transmitters and receivers, which output an optical
stream on one connector in a block and receive a return optical stream on the
second connector in the same block, the fiber optic I/O board uses one connector
on the block as an input and the second connector on the same block as a separate
output.
N
For proper cooling and air flow, boards and/or blank panels should be installed in
all locations during normal switcher operations.
Circuit boards can be replaced for fault correction or to accommodate SDI/HD-SDI
(electric) signals. They can be added or removed to increase or decrease the I/O
configuration (size) of the Fiber Matrix.
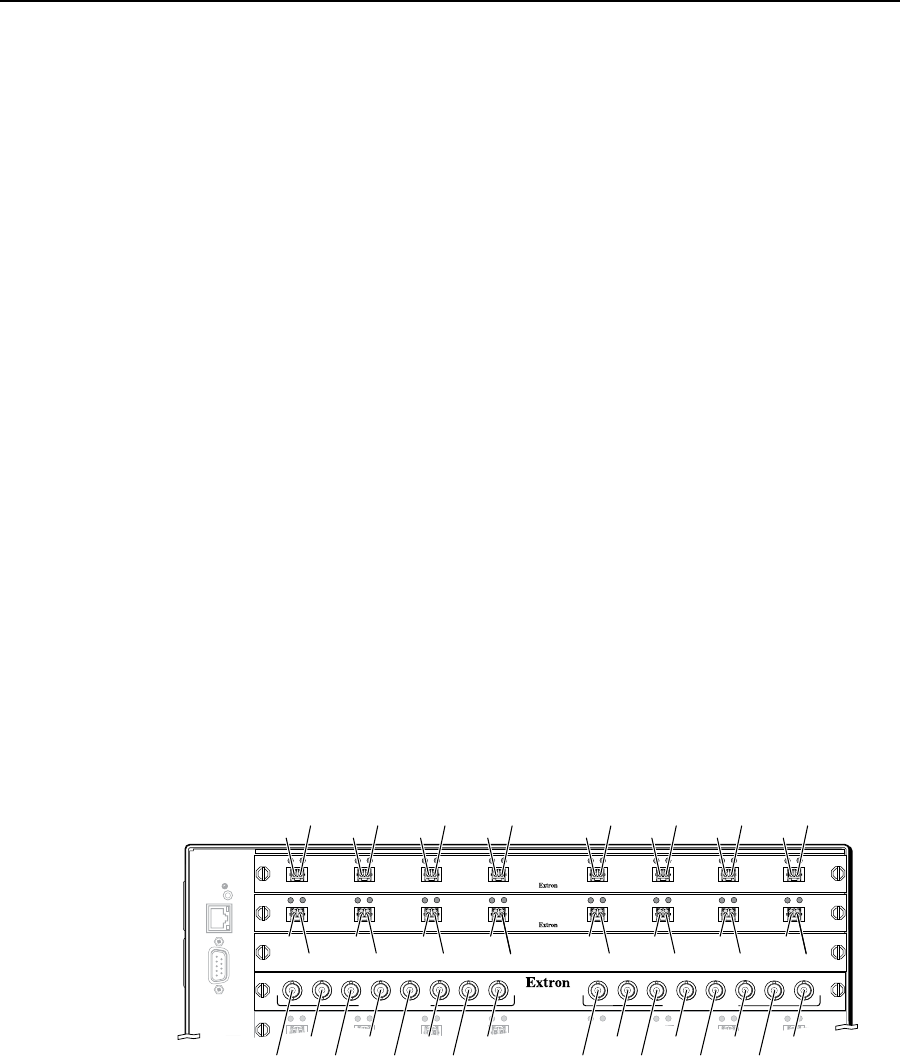
See figure 7-1. Each I/O board is identified by the input and output numbers supported
by the board position (1 - 8, 9 - 16, and so on) The transceiver modules on fiber optic
I/O boards and the BNC connectors on SDI/HD-SDI boards are identified as A through H.
RESET
RS232/RS422
REMOTE
LAN
ACT
LINK
1 - 8
9 - 16
17 - 24
25 - 3233 - 40
OUT
IN
A
OUT
IN
B
OUT
IN
C
OUT
IN
D
OUT
IN
E
OUT
IN
F
OUT
IN
G
OUT
IN
H
OUT
IN
A
OUT
IN
B
OUT
IN
C
OUT
IN
D
OUT
IN
E
OUT
IN
F
OUT
IN
G
OUT
IN
H
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
MUTI-RATE SDI INPUTS
H
G
AD
E
F
C
B
MUTI-RATE SDI OUTPUTS
H
G
AD
E
F
C
B
Slot 1
O#1
I#1
Slot 2
Slot 3
No board
installed
Slot 4
O#2
I#2
O#3
I#3
O#4
I#4
O#9
I#25
I#26
I#27
I#28
I#29
I#30
I#31
I#32
O#25
O#26
O#27
O#28
O#29
O#30
O#31
O#32
I#9
O#10
I#10
O#11
I#11
O#12
I#12
O#5
I#5
O#6
I#6
O#7
I#7
O#8
I#8
O#13
I#13
O#14
I#14
O#15
I#15
O#16
I#16
Figure 7-1 — Arrangement of inputs and outputs on the I/O boards
Locations A through H correspond to the input and output numbers identified
by the board position numbers. (For example, the input and output numbers
supported by the I/O board in location 17 - 24 are as follows: A = 17, B = 18, C = 19,
D = 20, E = 21, F = 22, G = 23, and H = 24.)
On the fiber optic I/O boards, locations A through H correspond to the transceiver
modules, each of which includes an input and an output. Therefore, locations A
through H are numbered from left to right.