Chapter 1 - Installation
1-12
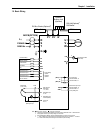
Wires and Terminal Lugs
Refer to the following table for wires, terminal lugs, and screws used to connect the inverter power input
(R, S, T) and output (U, V, W).
Wire
9
Ring Terminals
mm²
AWG
Inverter Capacity
Terminal
Screw Size
Screw
Torque
8
(Kgf·cm)/lb-in
R,S,T U,V,W R,S,T U,V,W R,S,T U,V,W
1 ~ 3 HP M3.5 15 / 10 2-4 2-4 2 2 14 14
5 HP M3.5 15 / 10 2-4 2-4 3.5 3.5 12 12
7.5 HP M4 15 / 10 5.5-5 5.5-5 5.5 5.5 10 10
10 HP M4 15 / 10 14-5 8-5 14 8 6 8
15 HP M5 26 / 18 14-5 14-5 14 14 6 6
20 HP M5 26 / 18 22-6 22-6 22 22 4 4
25 HP M6 45 / 31 38-8 38-8 30 30 2 2
200V
Class
30 HP M6 45 / 31 38-8 38-8 38 30 2 2
1 ~ 5 HP M3.5 15 / 10 2-4 2-4 2 2 14 14
7.5 HP M4 15 / 10 5.5-5 5.5-5 3.5 2 12 14
10 HP M4 15 / 10 14-5 8-5 3.5 3.5 12 12
15 HP M5 26 / 18 14-5 14-5 5.5 5.5 10 10
20 HP M5 26 / 18 22-6 22-6 14 8 6 8
25 HP M6 45 / 31 38-8 38-8 14 8 6 8
400V
Class
30 HP M6 45 / 31 38-8 38-8 22 14 4 6
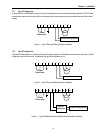
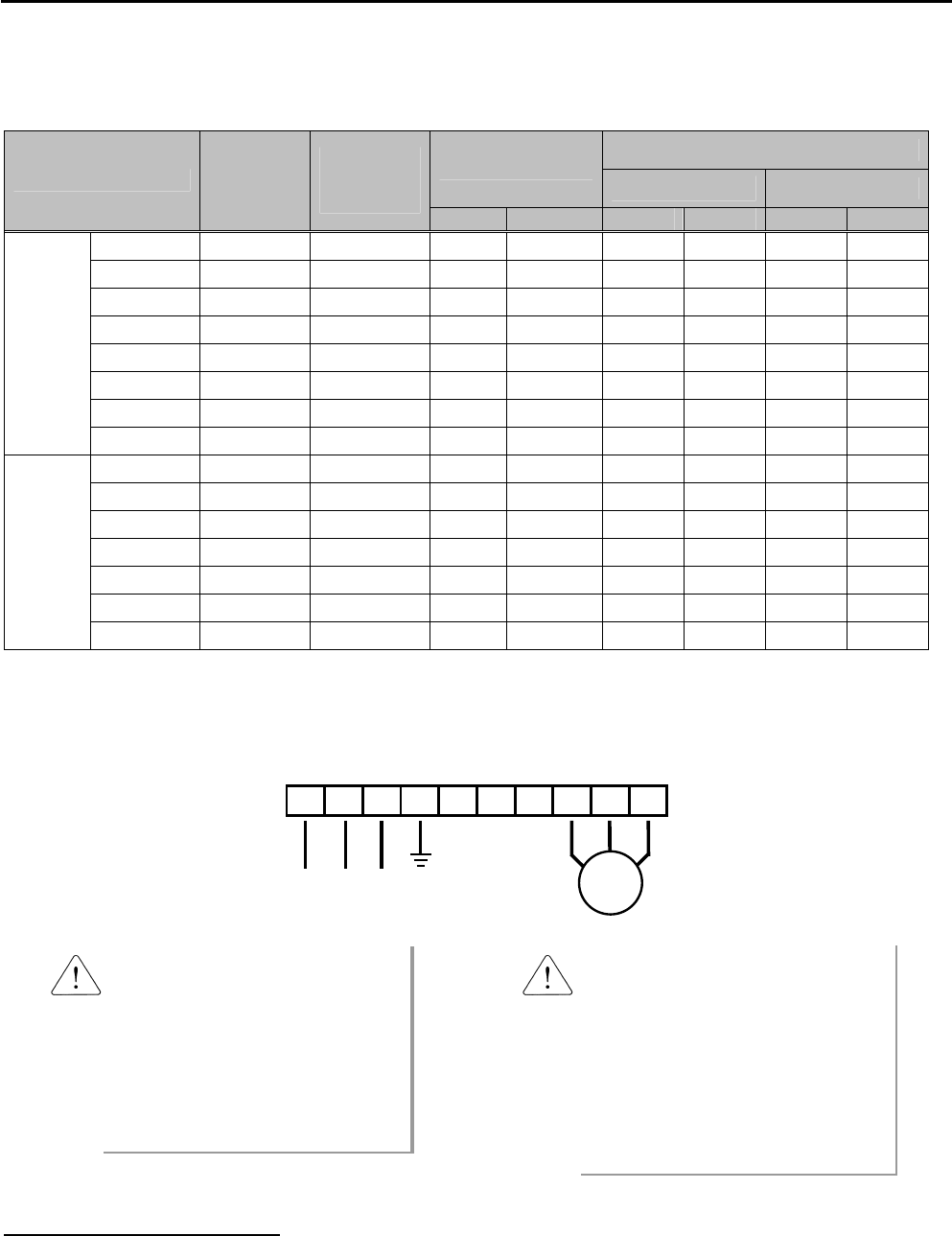
Power and Motor Connection
R S T G N B1 B2 U V W
8
Apply the rated torque to terminal screws. Loose screws can cause of short circuit or malfunction. Tightening the screws too much can
damage the terminals and cause a short circuit or malfunction.
9
Use copper wires only with 600V, 75℃ ratings.
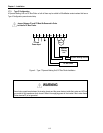
Motor
3 Phase
Power Input
Power supply must be connected
to the R, S, and T terminals.
Connecting it to the U, V, and W
terminals causes internal damages
to the inverter. Arranging the phase
sequence is not necessary.
Motor should be connected to the
U, V, and W terminals.
If the forward command (FX) is on,
the motor should rotate counter
clockwise when viewed from the load
side of the motor. If the motor rotates
in the reverse, switch the U and V
terminals.