Multiple Instance Spanning-Tree Operation
802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
(MSTP)
The 802.1D and 802.1w spanning tree protocols operate without regard to a
network’s VLAN configuration, and maintain one common spanning tree
throughout a bridged network. Thus, these protocols map one loop-free,
logical topology on a given physical topology. The 802.1s Multiple Spanning
Tree protocol (MSTP) uses VLANs to create multiple spanning trees in a
network, which significantly improves network resource utilization while
maintaining a loop-free environment.
While the per-VLAN spanning tree approach adopted by some vendors over-
comes the network utilization problems inherent in using STP or RSTP, using
a per-VLAN technology with multiple VLANs can overload the switch’s CPU.
MSTP on the switches covered in this guide complies with the IEEE 802.1s
standard, and extends STP and RSTP functionality to map multiple indepen-
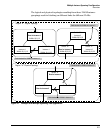
dent spanning tree instances onto a physical topology. With MSTP, each
spanning tree instance can include one or more VLANs and applies a separate,
per-instance forwarding topology. Thus, where a port belongs to multiple
VLANs, it may be dynamically blocked in one spanning tree instance, but
forwarding in another instance. This achieves load-balancing across the net-
work while keeping the switch’s CPU load at a moderate level (by aggregating
multiple VLANs in a single spanning tree instance). MSTP provides fault
tolerance through rapid, automatic reconfiguration if there is a failure in a
network’s physical topology.
With MSTP-capable switches, you can create a number of MST regions con-
taining multiple spanning tree instances. This requires the configuration of a
number of MSTP-capable switches. However, it is NOT necessary to do this.
You can just enable MSTP on an MSTP-capable switch and a spanning tree
instance is created automatically. This instance always exists by default when
spanning tree is enabled, and is the spanning tree instance that communicates
with STP and RSTP environments. The MSTP configuration commands oper-
ate exactly like RSTP commands and MSTP is backward-compatible with the
RSTP-enabled and STP-enabled switches in your network.
Caution Spanning tree interprets a switch mesh as a single link. Because the switch
automatically gives faster links a higher priority, the default MSTP parameter
settings are usually adequate for spanning tree operation. Also, because
incorrect MSTP settings can adversely affect network performance, you
should not change the MSTP settings from their default values unless you have
a strong understanding of how spanning tree operates.
4-6