Classifier-Based Software Configuration
Creating a Traffic Class
Note Although IPv4 and IPv6 masks are applied in opposite directions:
■ An IPv4 mask-length is applied from right to left, starting from the right-
most bits.
■ An IPv6 prefix-length is applied from left to right, starting from the
leftmost bits.
The behavior of IPv4 and IPv6 masks as match criteria and wildcards is the
same.
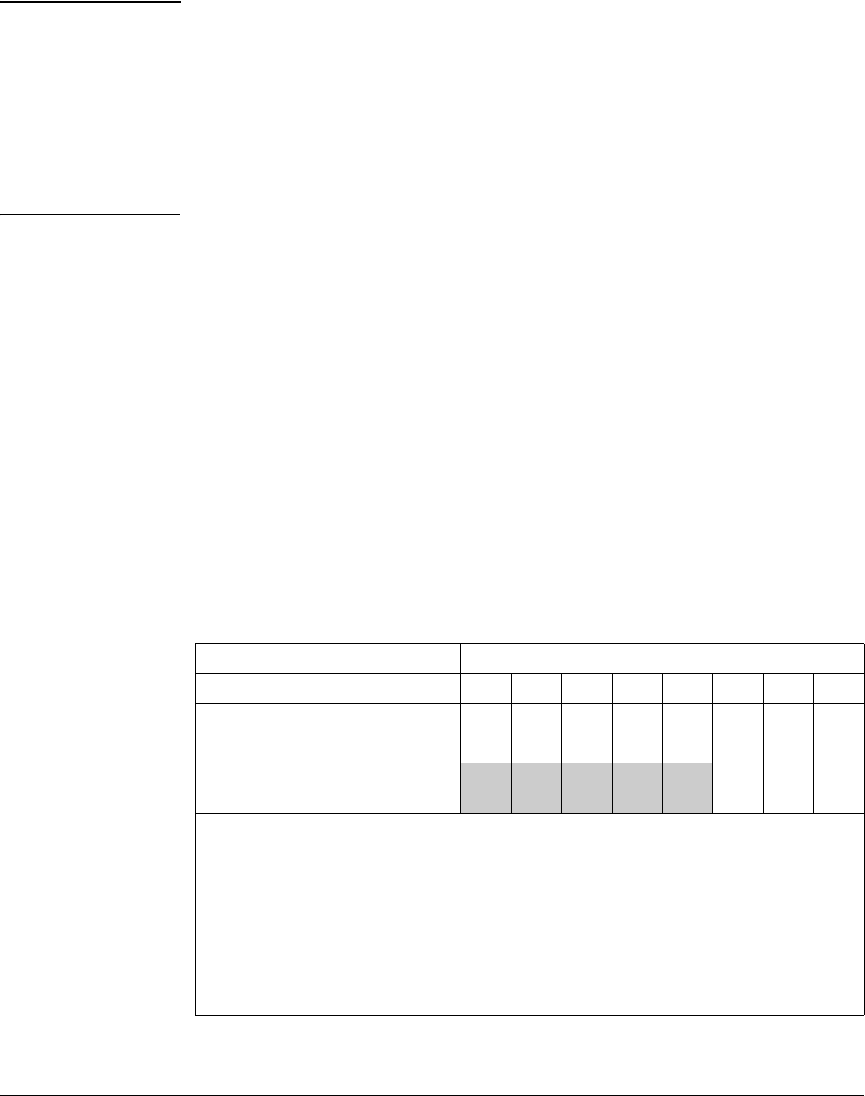
Example of How IPv4 Mask Bit Settings Define a Match. For this
example, the following configuration exists:
■ A match statement in a class configuration uses an IPv4 source-address/
mask-length of 10.38.31.125/21. The mask-length of 21 results in an IPv4
mask of 0.0.7.255. In the second octet of the mask, 7 means that the
rightmost three bits are “on”, or “1” (see the “Mask for SA” row in Table
9-3).
■ The second octet of the corresponding source address is 31, which means
that the rightmost five bits are “on”, or “1” (see the SA in Match Statement
row in Table 9-3).
In this example, a match occurs when the second octet of the SA in a packet
being classified has a value in the range of 24 (binary 00011000) to 31
(binary 00001111), as shown in the last row in Table 9-3.
Table 9-3. Example of How the IPv4 Mask Defines a Match
Location of Octet Bit Position in the Octet
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
SA in match statement
Mask for SA
Bits in the corresponding octet of a
packet’s SA that must exactly match
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0/1
1
1
0/1
1
1
0/1 0 0 0 1 1
The shaded area indicates the bits in the packet that must exactly match the bits in the source
IPv4 address in the match/ignore statement.
• If a mask bit is “1”(wildcard value), the corresponding bits in a source/destination address
in an IPv4 packet header can be any value.
• If a mask bit is “0”, the corresponding bits in a source/destination address must be the
same value as in the IPv4 address in the match/ignore statement.
Note: This example covers only one octet in an IPv4 address used as a match criterion. The
mask in a match/ignore statement may apply a packet filter to all four octets of a source/
destination address in IPv4 packet headers.
9-21


















