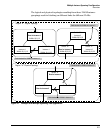
Multiple Instance Spanning-Tree Operation
802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
Terminology
BPDU — Acronym for bridge protocol data unit. BPDUs are data messages
that are exchanged between the switches within an extended LAN that use a
spanning tree protocol topology. BPDU packets contain information on ports,
addresses, priorities and costs and ensure that the data ends up where it was
intended to go. BPDU messages are exchanged across bridges to detect loops
in a network topology. The loops are then removed by placing redundant
switch ports in a backup, or blocked, state.
BPDU Filtering — Spanning-tree configuration mode that prevents the
switch from receiving and transmitting BPDU frames on a specific port (see
page 4-30 for details).
BPDU Protection — Spanning-tree configuration mode which disables a port
where BPDU frames are received (see page 4-31 for details).
Bridge: See “MSTP Bridge”.
Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST): Comprises all LANs, STP,
and RSTP bridges and MSTP regions in a network. The CIST automatically
determines the MST regions in a network and defines the root bridge (switch)
and designated port for each region. The CIST includes the Common Spanning
Tree (CST), the Internal Spanning Tree (IST) within each region, and any
multiple spanning-tree instances (MSTIs) in a region.
Common Spanning Tree (CST): Refers to the single forwarding path the
switch calculates for STP (802.1D) and RSTP (802.1w) topologies, and for
inter-regional paths in MSTP (802.1s) topologies. Note that all three types of
spanning tree can interoperate in the same network. Also, the MSTP switch
interprets a device running 802.1D STP or 802.1w RSTP as a separate region.
(Refer to figure 4-2 on page 4-7.)
Internal Spanning Tree (IST): Comprises all VLANs within a region that
are not assigned to a multiple spanning-tree instance configured within the
region. All MST switches in a region should belong to the IST. In a given region
“X”, the IST root switch is the regional root switch and provides information
on region “X” to other regions.
MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol): A network supporting MSTP
allows multiple spanning tree instances within configured regions, and a
single spanning tree among regions, STP bridges, and RSTP bridges.
4-13