Static Virtual LANs (VLANs)
General Steps for Using VLANs
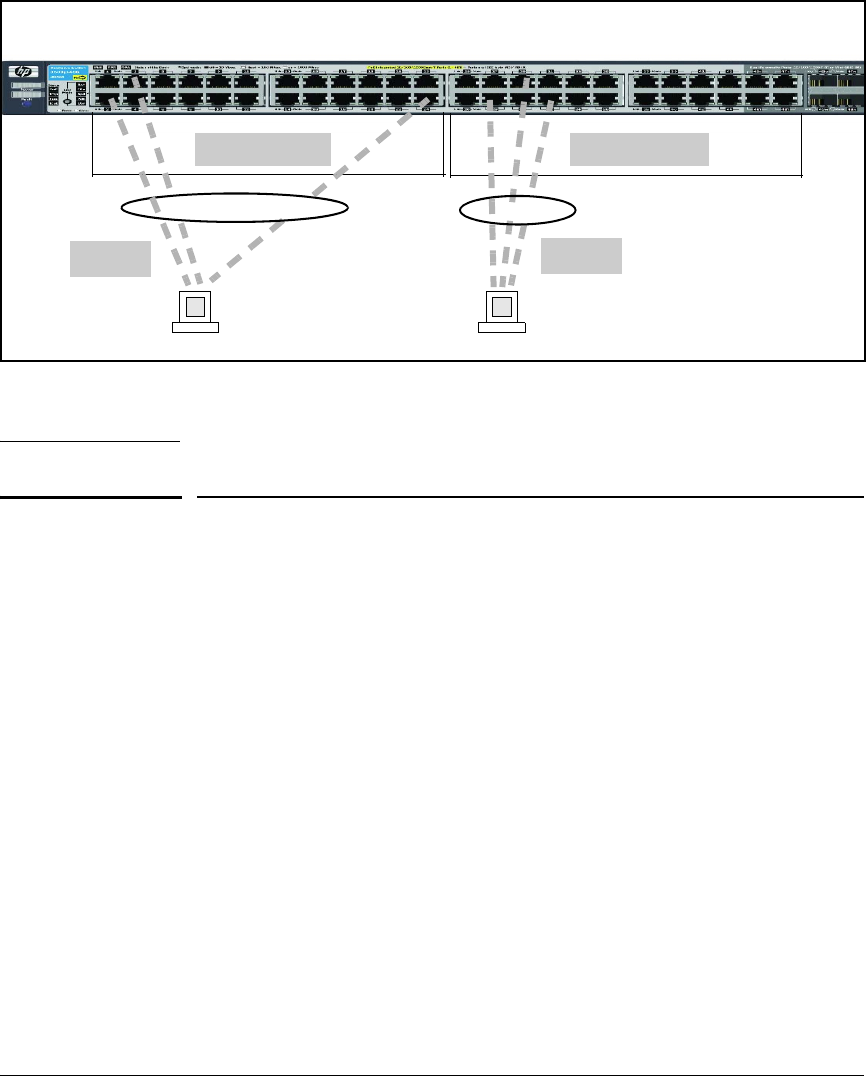
Port-bank 1-24 Port-bank 25-48
VLAN A
VLAN B
Figure 2-9. Example of VLANs Using Ports from the Same Port-Bank for Each VLAN
General Steps for Using VLANs
1. Plan your VLAN strategy and create a map of the logical topology that will
result from configuring VLANs. Include consideration for the interaction
between VLANs and other features such as Spanning Tree Protocol, port
trunking, and IGMP. (Refer to “Effect of VLANs on Other Switch Features”
on page 2-62.) If you plan on using dynamic VLANs, include the port
configuration planning necessary to support this feature. (Refer to chap-
ter 3, “GVRP” .)
By default, VLAN support is enabled for up to 256 VLANs.
2. Configure at least one VLAN in addition to the default VLAN.
3. Assign the desired switch ports to the new VLAN(s).
4. If you are managing VLANs with SNMP in an IP network, the VLAN
through which you are managing the switch must have an IP address. For
information on the procedure and restrictions when you configure an IP
address on a VLAN interface, refer to Table 2-1 on page 2-8.
2-19


















